Light and carbon: Synthetic biology toward new cyanobacteria-based living biomaterials
- PMID: 36846306
- PMCID: PMC9945787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100583
Light and carbon: Synthetic biology toward new cyanobacteria-based living biomaterials
Abstract
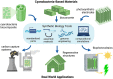
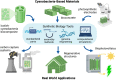
Cyanobacteria are ideal candidates to use in developing carbon neutral and carbon negative technologies; they are efficient photosynthesizers and amenable to genetic manipulation. Over the past two decades, researchers have demonstrated that cyanobacteria can make sustainable, useful biomaterials, many of which are engineered living materials. However, we are only beginning to see such technologies applied at an industrial scale. In this review, we explore the ways in which synthetic biology tools enable the development of cyanobacteria-based biomaterials. First we give an overview of the ecological and biogeochemical importance of cyanobacteria and the work that has been done using cyanobacteria to create biomaterials so far. This is followed by a discussion of commonly used cyanobacteria strains and synthetic biology tools that exist to engineer cyanobacteria. Then, three case studies-bioconcrete, biocomposites, and biophotovoltaics-are explored as potential applications of synthetic biology in cyanobacteria-based materials. Finally, challenges and future directions of cyanobacterial biomaterials are discussed.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Carbon sequestration; Cyanobacteria; Engineered living materials; Sustainability; Synthetic biology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Li F.-W., Brouwer P., Carretero-Paulet L., Cheng S., de Vries J., Delaux P.-M., Eily A., Koppers N., Kuo L.-Y., Li Z., Simenc M., Small I., Wafula E., Angarita S., Barker M.S., Bräutigam A., dePamphilis C., Gould S., Hosmani P.S., Huang Y.-M., Huettel B., Kato Y., Liu X., Maere S., McDowell R., Mueller L.A., Nierop K.G.J., Rensing S.A., Robison T., Rothfels C.J., Sigel E.M., Song Y., Timilsena P.R., Van de Peer Y., Wang H., Wilhelmsson P.K.I., Wolf P.G., Xu X., Der J.P., Schluepmann H., Wong G.K.-S., Pryer K.M. Fern genomes elucidate land plant evolution and cyanobacterial symbioses. Nat. Plants. 2018;4:460–472. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0188-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flombaum P., Gallegos J.L., Gordillo R.A., Rincón J., Zabala L.L., Jiao N., Karl D.M., Li W.K.W., Lomas M.W., Veneziano D., Vera C.S., Vrugt J.A., Martiny A.C. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013;110:9824–9829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307701110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell J.S., Foteinis S., Furey V., Hawrot O., Pike D., Aeschlimann S., Maesano C.N., Reginato P.L., Goodwin D.R., Looger L.L., Boyden E.S., Renforth P. Geochemical negative emissions technologies: Part I. Review. Front. Clim. 2022;4 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fclim.2022.879133 accessed. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

