The Usher syndrome 1C protein harmonin regulates canonical Wnt signaling
- PMID: 36846582
- PMCID: PMC9944737
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1130058
The Usher syndrome 1C protein harmonin regulates canonical Wnt signaling
Abstract
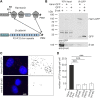
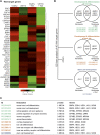
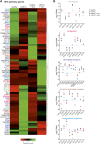
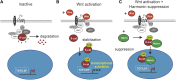
Human Usher syndrome (USH) is the most common form of hereditary combined deaf-blindness. USH is a complex genetic disorder, and the pathomechanisms underlying the disease are far from being understood, especially in the eye and retina. The USH1C gene encodes the scaffold protein harmonin which organizes protein networks due to binary interactions with other proteins, such as all USH proteins. Interestingly, only the retina and inner ear show a disease-related phenotype, although USH1C/harmonin is almost ubiquitously expressed in the human body and upregulated in colorectal cancer. We show that harmonin binds to β-catenin, the key effector of the canonical Wnt (cWnt) signaling pathway. We also demonstrate the interaction of the scaffold protein USH1C/harmonin with the stabilized acetylated β-catenin, especially in nuclei. In HEK293T cells, overexpression of USH1C/harmonin significantly reduced cWnt signaling, but a USH1C-R31* mutated form did not. Concordantly, we observed an increase in cWnt signaling in dermal fibroblasts derived from an USH1C R31*/R80Pfs*69 patient compared with healthy donor cells. RNAseq analysis reveals that both the expression of genes related to the cWnt signaling pathway and cWnt target genes were significantly altered in USH1C patient-derived fibroblasts compared to healthy donor cells. Finally, we show that the altered cWnt signaling was reverted in USH1C patient fibroblast cells by the application of Ataluren, a small molecule suitable to induce translational read-through of nonsense mutations, hereby restoring some USH1C expression. Our results demonstrate a cWnt signaling phenotype in USH establishing USH1C/harmonin as a suppressor of the cWnt/β-catenin pathway.
Keywords: USH1C; Usher syndrome; ataluren/PTC124; colorectal cancer; translational read-through; translational read-through inducing drugs; wnt signaling pathway; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2023 Schäfer, Wenck, Janik, Linnert, Stingl, Kohl, Nagel-Wolfrum and Wolfrum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of Unexpected Pathomechanisms Underlying the Human Usher Syndrome.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1468:171-175. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-76550-6_28. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39930191 Review.
-
Expression and subcellular localization of USH1C/harmonin in human retina provides insights into pathomechanisms and therapy.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Jan 13;32(3):431-449. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac211. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 35997788 Free PMC article.
-
Scaffold protein harmonin (USH1C) provides molecular links between Usher syndrome type 1 and type 2.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Dec 15;14(24):3933-43. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi417. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 16301216
-
Molecular basis of human Usher syndrome: deciphering the meshes of the Usher protein network provides insights into the pathomechanisms of the Usher disease.Exp Eye Res. 2006 Jul;83(1):97-119. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.11.010. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16545802 Review.
-
Photoreceptor expression of the Usher syndrome type 1 protein protocadherin 15 (USH1F) and its interaction with the scaffold protein harmonin (USH1C).Mol Vis. 2005 May 12;11:347-55. Mol Vis. 2005. PMID: 15928608
Cited by
-
The Role of Visual Electrophysiology in Systemic Hereditary Syndromes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 23;26(3):957. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030957. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of Human USH1C Transgene Expression Following Subretinal Injection in Wild-Type Pigs.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jan 2;66(1):48. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.1.48. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39836403 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Unexpected Pathomechanisms Underlying the Human Usher Syndrome.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1468:171-175. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-76550-6_28. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39930191 Review.
-
Enrichr-KG: bridging enrichment analysis across multiple libraries.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jul 5;51(W1):W168-W179. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad393. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37166973 Free PMC article.
-
Current approaches for Usher syndrome disease models and developing therapies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 20;13:1547523. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1547523. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40620763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angbohang A., Wu N., Charalambous T., Eastlake K., Lei Y., Kim Y. S., et al. (2016). Downregulation of the canonical WNT signaling pathway by TGFβ1 inhibits photoreceptor differentiation of adult human müller glia with stem cell characteristics. Stem Cells Dev. 25, 1–12. 10.1089/scd.2015.0262 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

