Probiotic potential of β‑galactosidase‑producing lactic acid bacteria from fermented milk and their molecular characterization
- PMID: 36846619
- PMCID: PMC9945298
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2023.1605
Probiotic potential of β‑galactosidase‑producing lactic acid bacteria from fermented milk and their molecular characterization
Abstract
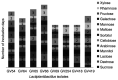
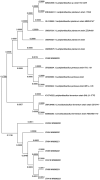
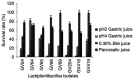
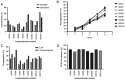
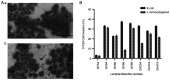
Probiotics have attained significant interest in recent years as a result of their gut microbiome modulation and gastrointestinal health benefits. Numerous fermented foods contain lactic acid bacteria (LAB) which are considered as GRAS and probiotic bacteria. The present study aimed to investigate indigenous LAB from homemade fermented milk samples collected in remote areas of Karnataka (India), in order to isolate the most potent and well-adapted to local environmental conditions bacteria, which were then evaluated using a step-by-step approach focused on the evaluation of probiotic traits and β-galactosidase-producing ability. LAB were screened using 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indole-D-galactopyranoside (X-Gal) and O-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) as substrate, and exhibited β-galactosidase activity ranging from 728.25 to 1,203.32 Miller units. The most promising isolates were selected for 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis and identified as Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Limosilactobacillus fermentum, Lactiplantibacillus pentosus and Lactiplantibacillus sp. Furthermore, these isolates were evaluated by in vitro, viz., survival in gastrointestinal tract, antibiotic susceptibility, antimicrobial activity, cell surface characteristics, and haemolytic activity. All eight isolates demonstrated strong adherence and prevented pathogen penetration into HT-29 cells, indicating potential of the bacteria to scale up industrial level production of milk products for lactose intolerants.
Keywords: GenBank; HT-29 cells; LAB; ONPG; X-Gal; lactose intolerance; probiotic; β-galactosidase.
Copyright: © Vasudha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probiotic attributes of indigenous Lactobacillus spp. isolated from traditional fermented foods and beverages of north-western Himalayas using in vitro screening and principal component analysis.J Food Sci Technol. 2016 May;53(5):2463-75. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2231-y. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Food Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 27407213 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional potentials of lactic acid bacterial isolates from Turkish traditional fermented foods.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2023 Jan 23;76(1):ovac012. doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovac012. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36688744
-
Genomic, biochemical and microbial evaluation of probiotic potentials of bacterial isolates from fermented sorghum products.Heliyon. 2021 Dec 2;7(12):e08536. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08536. eCollection 2021 Dec. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34926862 Free PMC article.
-
A novel approach to Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: From probiotic properties to the omics insights.Microbiol Res. 2023 Mar;268:127289. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127289. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Microbiol Res. 2023. PMID: 36571922 Review.
-
Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages.Food Nutr Res. 2016 Mar 8;60:29630. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v60.29630. eCollection 2016. Food Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 26960543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-strain Native Probiotics from the Asian Stinging Catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis) Enhance Growth, Blood Health, and Organ Morphology in the Host.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 May 9. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10540-3. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40343679
-
Alpha-amylase and alphaglucosidase inhibitory properties, beta-galactosidase activity, and probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria from Apis mellifera intermissa and its products.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 May 24;39(8):205. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03648-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37221413
-
Probiotic Characteristics and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Limosilactobacillus fermentum 664 Isolated from Chinese Fermented Pickles.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 7;13(6):703. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060703. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929142 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus (probiotic) with vitamin K3 and vitamin E on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: An in vitro pathogen model.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Jun;27(6):119. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13006. Epub 2023 May 5. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37144488 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic insights of lactic acid bacteria in reducing off-flavors and antinutrients in plant-based fermented dairy alternatives.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 Mar;24(2):e70134. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70134. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 40091739 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gayathri D, Vasudha M. Lactose Intolerance with Special Emphasis on Probiotics for Management. EC Nutrition. 2018;13:325–332.
-
- Sriphannam W, Lumyong S, Niumsap P, Ashida H, Yamamoto K, Khanongnuch C. A selected probiotic strain of Lactobacillus fermentum CM33 isolated from breast-fed infants as a potential source of β-galactosidase for prebiotic oligosaccharide synthesis. J Microbiol. 2012;50:119–126. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-1108-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
