Formulation and physicochemical characterization of azithromycin-loaded cubosomes
- PMID: 36846738
- PMCID: PMC9951788
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.363595
Formulation and physicochemical characterization of azithromycin-loaded cubosomes
Abstract
Background and purpose: Azithromycin (AZ) is a macrolide antibiotic that is soluble in saliva pH; its bitter taste can be well sensed, decreasing the ability of the patient to get the drug. Thus, handling such a bitter taste is challenging in developing the oral formulation. A wide range of methods has been applied to tackle this problem. Cubosomes are considered nanoparticles forming cubic three-dimensional structures with a taste-masking effect. This research aimed to apply cubosomes to mask AZ's bitter taste.
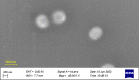
Experimental approach: Cubosomes which contained AZ were obtained by applying the film hydration method. Design expert software (version 11) was then employed for optimizing cubosomes that contained the drug. The encapsulation efficiency, particle size as well as polydispersity index of drug-loaded cubosomes were then subjected to evaluation. Assessment of particle morphology was done through SEM. The antimicrobial qualities of AZ-loaded cubosomes were then assessed by utilizing the disc diffusion method. Then, the taste masking study was carried out by referring to human volunteers.
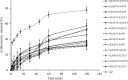
Finding/results: AZ-loaded cubosomes were spherical in terms of shape and in the 166-272 nm range, with a polydispersity index of 0.17-0.33 and encapsulation efficiency of 80-92%. The results related to the microbial culture revealed that the antimicrobial qualities related to AZ-loaded cubosomes were like those of AZ. The results obtained by taste evaluation also revealed that the cubosomes could well mask the drug's bitter taste.
Conclusion and implications: These findings, thus, revealed that while the antimicrobial impact of AZ is not under the influence of loading in cubosomes, its taste could be well improved.
Keywords: Azithromycin; Cubosomes; Oral delivery; Taste masking.
Copyright: © 2022 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new strategy for taste masking of azithromycin antibiotic: development, characterization, and evaluation of azithromycin titanium nanohybrid for masking of bitter taste using physisorption and panel testing studies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Nov 8;12:3855-3866. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S183534. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30510401 Free PMC article.
-
Taste-masking and colloidal-stable cubosomes loaded with Cefpodoxime proxetil for pediatric oral delivery.Int J Pharm. 2020 Feb 15;575:118875. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118875. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31765781
-
Formulation and biopharmaceutical evaluation of bitter taste masking microparticles containing azithromycin loaded in dispersible tablets.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 May;126:187-200. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.03.017. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 28359878
-
Cubosomes: Versatile Nanosized Formulation for Efficient Delivery of Therapeutics.Curr Drug Deliv. 2022;19(6):644-657. doi: 10.2174/1567201818666210708123855. Curr Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 34238187 Review.
-
A review on the taste masking of bitter APIs: hot-melt extrusion (HME) evaluation.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2014 Feb;40(2):145-56. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2013.804833. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2014. PMID: 23763436 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and In Vitro Characterization of Azithromycin-PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded Thermoresponsive Hydrogels: A Quality by Design Approach Toward Intra-Articular Delivery of Macrolides.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Jun 26;26(6):171. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03170-z. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40571801
-
Preparation of PLA Nanoparticles and Study of Their Influencing Factors.Molecules. 2024 Nov 25;29(23):5566. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235566. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khanmohamadi A, Valizadeh H, Azhdarzadeh M, Lotfipur F, Mohammadi G, Zakeri P. Antibacterial evaluation of azithromycin nanoparticles. Res Pharm Sci. 2012;7(5):14.
-
- Abou Assi R, Abdulbaqi IM, Ming TS, Yee CS, Wahab HA, Asif SM, et al. Liquid and solid self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDs) as carriers for the oral delivery of azithromycin: optimization, in vitro characterization and stability assessment. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(11):1–29. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111052. 1052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saberi A, Jafari AZ, Mortazavi S. Formulation and evaluation of domperidone fast disintegrating tablets and its taste masking using solid dispersion technology. Res Pharm Sci. 2012;7(5):341.
-
- Amin F, Khan S, Shah SMH, Rahim H, Hussain Z, Sohail M, et al. A new strategy for taste masking of azithromycin antibiotic: development, characterization, and evaluation of azithromycin titanium nanohybrid for masking of bitter taste using physisorption and panel testing studies. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:3855–3866. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S183534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
