THINGS-data, a multimodal collection of large-scale datasets for investigating object representations in human brain and behavior
- PMID: 36847339
- PMCID: PMC10038662
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.82580
THINGS-data, a multimodal collection of large-scale datasets for investigating object representations in human brain and behavior
Abstract
Understanding object representations requires a broad, comprehensive sampling of the objects in our visual world with dense measurements of brain activity and behavior. Here, we present THINGS-data, a multimodal collection of large-scale neuroimaging and behavioral datasets in humans, comprising densely sampled functional MRI and magnetoencephalographic recordings, as well as 4.70 million similarity judgments in response to thousands of photographic images for up to 1,854 object concepts. THINGS-data is unique in its breadth of richly annotated objects, allowing for testing countless hypotheses at scale while assessing the reproducibility of previous findings. Beyond the unique insights promised by each individual dataset, the multimodality of THINGS-data allows combining datasets for a much broader view into object processing than previously possible. Our analyses demonstrate the high quality of the datasets and provide five examples of hypothesis-driven and data-driven applications. THINGS-data constitutes the core public release of the THINGS initiative (https://things-initiative.org) for bridging the gap between disciplines and the advancement of cognitive neuroscience.
Keywords: MEG; behavior; fMRI; human; neuroscience; objects; research data; vision.
Conflict of interest statement
MH, OC, LT, AR, CZ, AK, AC, MV No competing interests declared, CB Senior editor, eLife
Figures

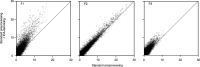
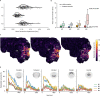

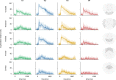


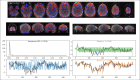


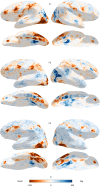
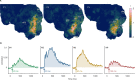

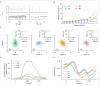
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2022.07.22.501123
References
-
- Allen EJ, St-Yves G, Wu Y, Breedlove JL, Prince JS, Dowdle LT, Nau M, Caron B, Pestilli F, Charest I, Hutchinson JB, Naselaris T, Kay K. A massive 7T fMRI dataset to bridge cognitive neuroscience and artificial intelligence. Nature Neuroscience. 2022;25:116–126. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00962-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

