The influence of foreperiod duration on the preparation and control of sequential aiming movements
- PMID: 36847427
- PMCID: PMC10798029
- DOI: 10.1177/17470218231162617
The influence of foreperiod duration on the preparation and control of sequential aiming movements
Abstract
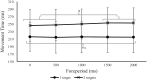
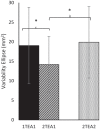
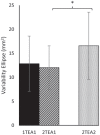
Reaction time (RT) and movement times (MTs) to the first target are typically longer for two-target sequential movements compared to one-target movements. While this one-target advantage has been shown to be dependent on the availability of advance information about the numbers of targets, there has been no systematic investigation of how foreperiod duration (i.e., interval between presentation of the target(s) and stimulus) influences the planning and execution of sequential movements. Two experiments were performed to examine how the one-target advantage is influenced by the availability and timing of advance target information. In Experiment 1, participants performed one- and two-target movements in two separate blocks. In Experiment 2, target conditions were randomised from trial to trial. The interval between target(s) appearing and stimulus tone (i.e., foreperiod) was varied randomly (0, 500, 1,000, 1,500, and 2,000 ms). The results of Experiment 1 revealed that while the one-target advantage in RT was not influenced by foreperiod duration, the one-target advantage in MT increased as foreperiod duration increased. The variability of endpoints at the first target was greater in the two- compared to one-target condition. In Experiment 2, the one-target advantage in both RT and MT increased as the length of the foreperiod increased. However, there was no difference in limb trajectory variability between target conditions. The implication of these findings for theories of motor planning and execution of multiple segment movements is discussed.
Keywords: Sequential aiming movements; movement control; movement planning; response complexity.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures






References
-
- Adam J. J., Helsen W. F., Elliott D., Beukers M. J. (2001). The one-target advantage on the control of rapid sequential aiming movements: The effect of practice. Journal of Human Movement Studies, 41, 301–313.
-
- Adam J. J., Paas F. G. W. C. (1996). Dwell time in reciprocal aiming tasks. Human Movement Science, 15, 1–24.
-
- Adam J. J., Paas F. G. W. C., Eyssem I. C. J. M., Slingerland H., Bekkering H., Drost M. R. (1995). The control of two-element, reciprocal aiming movements: Evidence of chunking. Human Movement Science, 14, 1–11.
-
- Adam J. J., van der Bruggen D. P. W., Bekkering H. (1993). The control of discrete and reciprocal aiming responses: Evidence for the exploitation of mechanics. Human Movement Science, 12, 353–364.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

