The Effects of Opt-out vs Opt-in Tobacco Treatment on Engagement, Cessation, and Costs: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 36848129
- PMCID: PMC9972241
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.7170
The Effects of Opt-out vs Opt-in Tobacco Treatment on Engagement, Cessation, and Costs: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Tobacco use causes 7 million deaths per year; most national guidelines require people who use tobacco to opt in to care by affirming they are willing to quit. Use of medications and counseling is low even in advanced economy countries.
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of opt-out care vs opt-in care for people who use tobacco.
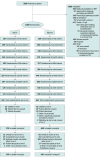
Design, setting, and participants: In Changing the Default (CTD), a Bayesian adaptive population-based randomization trial, eligible patients were randomized into study groups, treated according to group assignment, and debriefed and consented for participation at 1-month follow-up. A total of 1000 adult patients were treated at a tertiary care hospital in Kansas City. Patients were randomized from September 2016 to September 2020; final follow-up was in March 2021.
Interventions: At bedside, counselors screened for eligibility, conducted baseline assessment, randomized patients to study group, and provided opt-out care or opt-in care. Counselors and medical staff provided opt-out patients with inpatient nicotine replacement therapy, prescriptions for postdischarge medications, a 2-week medication starter kit, treatment planning, and 4 outpatient counseling calls. Patients could opt out of any or all elements of care. Opt-in patients willing to quit were offered each element of treatment described previously. Opt-in patients who were unwilling to quit received motivational counseling.
Main outcomes and measures: The main outcomes were biochemically verified abstinence and treatment uptake at 1 month after randomization.
Results: Of a total of 1000 eligible adult patients who were randomized, most consented and enrolled (270 [78%] of opt-in patients; 469 [73%] of opt-out patients). Adaptive randomization assigned 345 (64%) to the opt-out group and 645 (36%) to the opt-in group. The mean (SD) age at enrollment was 51.70 (14.56) for opt-out patients and 51.21 (14.80) for opt-out patients. Of 270 opt-in patients, 123 (45.56%) were female, and of 469 opt-out patients, 226 (48.19%) were female. Verified quit rates for the opt-out group vs the opt-in group were 22% vs 16% at month 1 and 19% vs 18% at 6 months. The Bayesian posterior probability that opt-out care was better than opt-in care was 0.97 at 1 month and 0.59 at 6 months. Treatment use for the opt-out group vs the opt-in group was 60% vs 34% for postdischarge cessation medication (bayesian posterior probability of 1.0), and 89% vs 37% for completing at least 1 postdischarge counseling call (bayesian posterior probability of 1.0). The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $678.60, representing the cost of each additional quit in the opt-out group.
Conclusions and relevance: In this randomized clinical trial, opt-out care doubled treatment engagement and increased quit attempts, while enhancing patients' sense of agency and alliance with practitioners. Stronger and longer treatment could increase cessation.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02721082.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2017: monitoring tobacco use and prevention policies. 2017. Accessed March 27, 2022. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/255874
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services . Interventions for smoking cessation and treatments for nicotine dependence. 2020. Accessed January 21, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/sgr/2020-smoking-cessation/pdfs/2020-cessati...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

