Immunogenicity of peptide-based vaccine composed of epitopes from Echinococcus granulosus rEg.P29
- PMID: 36848174
- PMCID: PMC11977596
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202201636R
Immunogenicity of peptide-based vaccine composed of epitopes from Echinococcus granulosus rEg.P29
Abstract
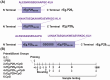
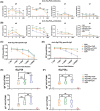
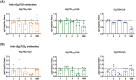
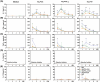
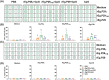
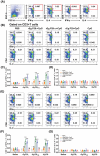
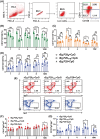
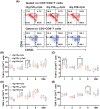
Echinococcus granulosus is one of the main causes of economic loss in the livestock industry because of its food-borne transmission. Cutting off the transmission route is a valid prevention method, and vaccines are the most effective means of controlling and eliminating infectious diseases. However, no human-related vaccine has been yet marketed. As a genetic engineering vaccine, recombinant protein P29 of E. granulosus (rEg.P29) could provide protection against deadly challenges. In this study, we generated peptide vaccines (rEg.P29T , rEg.P29B , and rEg.P29T+B ) based on rEg.P29 and an immunized model was established by subcutaneous immunization. Further evaluation showed that peptide vaccine immunization in mice induced T helper type 1 (Th1)-mediated cellular immune responses, leading to high levels of rEg.P29 or rEg.P29B -specific antibodies. In addition, rEg.P29T+B immunization can induce a higher antibody and cytokine production level than single-epitope vaccines, and immune memory is also longer. Collectively, these results suggest that rEg.P29T+B has the potential to be developed as an efficient subunit vaccine for use in areas where E. granulosus is endemic.
Keywords: E. granulosus; Th1 cells; antibody; immune memory; immunogenicity; peptide vaccine.
© 2023 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthetic rEg.P29 Peptides Induce Protective Immune Responses Against Echinococcus granulosus in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Mar 3;13(3):266. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030266. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266142 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing sheep B-cell epitopes in Echinococcus granulosus recombinant antigen P29 for vaccine development.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1451538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451538. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39206186 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in intestinal flora of mice induced by rEg.P29 epitope peptide vaccines.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Nov;11(11):e1082. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1082. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38018604 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and future prospective of vaccine development against Echinococcus granulosus.Biologicals. 2018 Jan;51:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2017.10.003. Biologicals. 2018. PMID: 29100669 Review.
-
Current situation and future prospects of Echinococcus granulosus vaccine candidates: A systematic review.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 May;68(3):1080-1096. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13772. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 32762075
Cited by
-
Host Proteins in Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestodes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 1;26(7):3266. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073266. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244114 Free PMC article.
-
Basic Operative Tactics for Pulmonary Echinococcosis in the Era of Endostaplers and Energy Devices.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Mar 10;59(3):543. doi: 10.3390/medicina59030543. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36984545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic rEg.P29 Peptides Induce Protective Immune Responses Against Echinococcus granulosus in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Mar 3;13(3):266. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030266. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266142 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing sheep B-cell epitopes in Echinococcus granulosus recombinant antigen P29 for vaccine development.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1451538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451538. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39206186 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a novel EmTSP-3 and EmTIP based multi-epitope vaccine against Echinococcus multilocularis infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 16;15:1425603. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425603. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39351224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lightowlers MW, Gasser RB, Hemphill A, et al. Advances in the treatment, diagnosis, control and scientific understanding of taeniid cestode parasite infections over the past 50 years. Int J Parasitol. 2021;51:1167‐1192. - PubMed
-
- Woolsey ID, Miller AL. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato and Echinococcus multilocularis: a review. Res Vet Sci. 2021;135:517‐522. - PubMed
-
- Tamarozzi F, Deplazes P, Casulli A. Reinventing the wheel of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato transmission to humans. Trends Parasitol. 2020;36:427‐434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

