Weakly Supervised Captioning of Ultrasound Images
- PMID: 36848308
- PMCID: PMC7614238
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-12053-4_14
Weakly Supervised Captioning of Ultrasound Images
Abstract
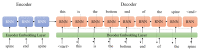
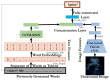
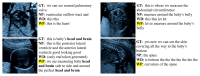
Medical image captioning models generate text to describe the semantic contents of an image, aiding the non-experts in understanding and interpretation. We propose a weakly-supervised approach to improve the performance of image captioning models on small image-text datasets by leveraging a large anatomically-labelled image classification dataset. Our method generates pseudo-captions (weak labels) for caption-less but anatomically-labelled (class-labelled) images using an encoder-decoder sequence-to-sequence model. The augmented dataset is used to train an image-captioning model in a weakly supervised learning manner. For fetal ultrasound, we demonstrate that the proposed augmentation approach outperforms the baseline on semantics and syntax-based metrics, with nearly twice as much improvement in value on BLEU-1 and ROUGE-L. Moreover, we observe that superior models are trained with the proposed data augmentation, when compared with the existing regularization techniques. This work allows seamless automatic annotation of images that lack human-prepared descriptive captions for training image-captioning models. Using pseudo-captions in the training data is particularly useful for medical image captioning when significant time and effort of medical experts is required to obtain real image captions.
Keywords: Data Augmentation; Fetal Ultrasound; Image Captioning.
Figures
References
-
- Google code archive. 2018. https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/
-
- Evaluating models — automl translation documentation. 2020. https://cloud.google.com/translate/automl/docs/evaluate .
-
- Grammarbot. 2020. https://www.grammarbot.io/
-
- Textblob. 2020. https://textblob.readthedocs.io/en/dev/
-
- Context analysis in nlp: why it’s valuable and how it’s done. 2021. https://www.lexalytics.com/lexablog/context-analysis-nlp .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
