Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Normal Aging and Neurodegeneration: Mechanisms, Impact, and Treatments
- PMID: 36848419
- PMCID: PMC9993074
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.040578
Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Normal Aging and Neurodegeneration: Mechanisms, Impact, and Treatments
Abstract
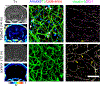
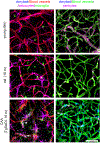
Cerebral endothelial cells and their linking tight junctions form a unique, dynamic and multi-functional interface, the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The endothelium is regulated by perivascular cells and components forming the neurovascular unit. This review examines BBB and neurovascular unit changes in normal aging and in neurodegenerative disorders, particularly focusing on Alzheimer disease, cerebral amyloid angiopathy and vascular dementia. Increasing evidence indicates BBB dysfunction contributes to neurodegeneration. Mechanisms underlying BBB dysfunction are outlined (endothelium and neurovascular unit mediated) as is the BBB as a therapeutic target including increasing the uptake of systemically delivered therapeutics across the BBB, enhancing clearance of potential neurotoxic compounds via the BBB, and preventing BBB dysfunction. Finally, a need for novel biomarkers of BBB dysfunction is addressed.
Keywords: aging; blood-brain barrier; cerebral amyloid angiopathy; neurodegeneration; neurovascular unit; vascular dementia.
Figures


References
-
- Corriveau RA, Bosetti F, Emr M, Gladman JT, Koenig JI, Moy CS, Pahigiannis K, Waddy SP, Koroshetz W. The Science of Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia (VCID): A Framework for Advancing Research Priorities in the Cerebrovascular Biology of Cognitive Decline. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016;36:281–288. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0334-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

