2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1 H-benzo[ d]imidazole as a Promising Template for the Development of Metabolically Robust, α1β2γ2GABA-A Receptor-Positive Allosteric Modulators
- PMID: 36848624
- PMCID: PMC10020958
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00800
2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1 H-benzo[ d]imidazole as a Promising Template for the Development of Metabolically Robust, α1β2γ2GABA-A Receptor-Positive Allosteric Modulators
Abstract
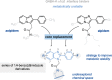
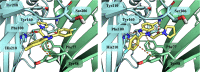
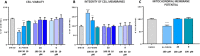
Modulation of α1β2γ2GABA-A receptor subpopulation expressed in the basal ganglia region is a conceptually novel mode of pharmacological strategy that offers prospects to tackle a variety of neurological dysfunction. Although clinical findings provided compelling evidence for the validity of this strategy, the current chemical space of molecules able to modulate the α1/γ2 interface of the GABA-A receptor is limited to imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives that undergo rapid biotransformation. In response to a deficiency in the chemical repertoire of GABA-A receptors, we identified a series of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazoles as positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) with improved metabolic stability and reduced potential for hepatotoxicity, where lead molecules 9 and 23 displayed interesting features in a preliminary investigation. We further disclose that the identified scaffold shows a preference for interaction with the α1/γ2 interface of the GABA-A receptor, delivering several PAMs of the GABA-A receptor. The present work provides useful chemical templates to further explore the therapeutic potential of GABA-A receptor ligands and enriches the chemical space of molecules suitable for the interaction with the α1/γ2 interface.
Keywords: 1H-benzo[d]imidazole; GABA-A receptor; benzodiazepine site; positive allosteric modulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



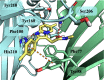
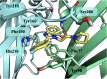
References
-
- Daniele A.; Panza F.; Greco A.; Logroscino G.; Seripa D. Can a Positive Allosteric Modulation of GABAergic Receptors Improve Motor Symptoms in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease? The Potential Role of Zolpidem in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinson’s Dis. 2016, 2016, 1–14. 10.1155/2016/2531812. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

