Case Report: Reemerging Paragonimiasis in Umphang District, Thailand
- PMID: 36848893
- PMCID: PMC10077016
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0708
Case Report: Reemerging Paragonimiasis in Umphang District, Thailand
Abstract
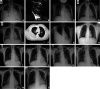
Paragonimiasis is a food-born zoonotic parasitosis caused by Paragonimus spp. Six cases of reemerging paragonimiasis within the Karan hill-tribe near the Thai-Myanmar border were evaluated to review clinical manifestations, predisposing factors, and treatment regimens. All patients tested positive for paragonimiasis eggs and presented with an array of symptoms, including chronic cough, hemoptysis, peripheral eosinophilia, and thoracic radiograph abnormalities. All fully recovered after a 2- to 5-day course of 75 to 80 mg/kg/day praziquantel. We conclude that paragonimiasis should be considered during differential diagnoses to promote early treatment and to prevent misdiagnosis of reemerging or sporadic cases. This applies particularly to endemic regions and high-risk groups known to habitually consume raw or undercooked intermediate or paratenic hosts.
Figures

References
-
- Richter J, 2022. Current status of the treatment of paragonimiasis. One Health Implement Res 2: 96–107.
-
- Yoonuan T, Vanvanitchai Y, Dekumyoy P, Komalamisra C, Kojima S, Waikagul J, 2008. Paragonimiasis prevalences in Saraburi Province, Thailand, measured 20 years apart. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 39: 593–600. - PubMed
-
- Watthanakulpanich D, Waikagul J, Dekumyoy P, Muangkhum P, Praevanit R, Mongkhonmu S, 2005. Case report: paragonimiasis in Nan Province, northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 36: 853–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

