Evaluation of an immunochromatography-based rapid antigen test, Inspecter Kowa® SARS-CoV-2, using saliva specimens for the detection of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36849098
- PMCID: PMC9968476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2023.02.011
Evaluation of an immunochromatography-based rapid antigen test, Inspecter Kowa® SARS-CoV-2, using saliva specimens for the detection of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: In the context of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a rapid and reliable point-of-care test is an essential tool for controlling the spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In particular, an immunochromatography test (ICT) that uses saliva specimens for rapid antigen detection not only reduces the risk of secondary infections but also reduces the burden on medical personnel.
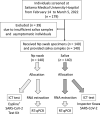
Methods: The newly developed salivary antigen test kit "Inspecter Kowa® SARS-CoV-2" is an ICT to which saliva specimens can be directly applied. We evaluated its usefulness in comparison with reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and the Espline® SARS-CoV-2 Kit for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 using nasopharyngeal swab specimens. In this study, 140 patients with suspected symptomatic COVID-19 who visited our hospital were enrolled, and nasopharyngeal swab and saliva specimens were collected after they consented to participate in the study.
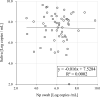
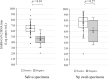
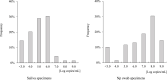
Results: Inspector Kowa SARS-CoV-2 was positive in 45 of 61 (73.8%) saliva that were positive by RT-qPCR and the Espline® SARS-CoV-2 Kit was also positive in 56 of 60 (93.3%) Np swabs that were positive by RT-qPCR. Good antigen detection was achieved by ICT with saliva and nasopharyngeal swab specimens when viral load was ≥105 copies/mL, whereas detection sensitivity was low when viral load was <105 copies/mL, especially in saliva specimens.
Conclusion: This ICT for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 salivary antigen is an attractive tool that does not require specialized equipment and allows patients to perform the entire process from sample collection to self-diagnose and to reduce the burden on medical care during a pandemic.
Keywords: Antigen detection; COVID-19; Immunochromatography; SARS-CoV-2; Saliva.
Copyright © 2023 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy, Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases, and Japanese Society for Infection Prevention and Control. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures
References
-
- WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Jayakody H., Kiddle G., Perera S., Tisi L., Leese L.S. Molecular diagnostics in the era of COVID-19. Anal Methods. 2021;13(34):3744–3763. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

