The effect of micro-particle curcumin on chronic kidney disease progression: the MPAC-CKD randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 36849161
- PMCID: PMC10539205
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfad037
The effect of micro-particle curcumin on chronic kidney disease progression: the MPAC-CKD randomized clinical trial
Abstract
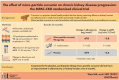
Background: Curcumin is a commonly used herbal supplement with anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties. Animal studies and small human trials suggest that curcumin reduces albuminuria in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Micro-particle curcumin is a new, more bioavailable formulation of curcumin.
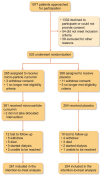
Methods: To determine whether micro-particle curcumin versus placebo slows the progression of albuminuric CKD we conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 6-month follow-up. We included adults with albuminuria [a random urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio >30 mg/mmol (265 mg/g) or a 24-h urine collection with more than 300 mg of protein] and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) between 15 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 within the 3 months before randomization. We randomly allocated participants 1:1 to receive micro-particle curcumin capsules (90 mg/day) or matching placebo for 6 months. After randomization, the co-primary outcomes were the changes in albuminuria and the eGFR.
Results: We enrolled 533 participants, but 4/265 participants in the curcumin group and 15/268 in the placebo group withdrew consent or became ineligible. The 6-month change in albuminuria did not differ significantly between the curcumin and placebo groups [geometric mean ratio 0.94, 97.5% confidence interval (CI) 0.82 to 1.08, P = .32]. Similarly, the 6-month change in eGFR did not differ between groups (mean between-group difference -0.22 mL/min/1.73 m2, 97.5% CI -1.38 to 0.95, P = .68).
Conclusions: Ninety milligrams of micro-particle curcumin daily did not slow the progression of albuminuric CKD over 6 months.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02369549.
Keywords: GFR; albuminuria; chronic renal insufficiency; clinical trial; curcumin.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The results presented in this paper have not been published previously in whole or part.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous