Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 36849642
- PMCID: PMC11087144
- DOI: 10.1007/s11914-023-00779-6
Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
Purpose of review: This study aims to review diagnosis, potential complications, and clinical management in craniofacial fibrous dysplasia.
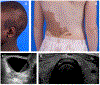
Recent findings: Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a rare mosaic disorder in which normal bone and marrow are replaced with expansile fibro-osseous lesions. Disease presents along a broad spectrum and may be associated with extraskeletal features as part of McCune-Albright syndrome (MAS). The craniofacial skeleton is one of the most commonly impacted areas in FD, and its functional and anatomical complexities create unique challenges for diagnosis and management. This review summarizes current approaches to diagnosis and management in FD/MAS, with emphasis on the clinical and therapeutic implications for the craniofacial skeleton.
Keywords: Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia; Fibrous dysplasia; McCune Albright syndrome; Rare bone disease.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Boyce AM, Florenzano P, de Castro LF, Collins MT. Fibrous Dysplasia / McCune-Albright Syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 2015. pp. 1993–2023. - PubMed
-
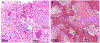
- Riminucci M, Liu B, Corsi A, et al. The histopathology of fibrous dysplasia of bone in patients with activating mutations of the Gs alpha gene: site-specific patterns and recurrent histological hallmarks. J Pathol. 1999;187(2):249–58. 10.1002/(sici)1096-9896(199901)187:2<249::Aid-path222>3.0.Co;2-j. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

