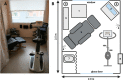
The Berlin-Buch respiration chamber for energy expenditure measurements
- PMID: 36849666
- PMCID: PMC10192165
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-023-05164-w
The Berlin-Buch respiration chamber for energy expenditure measurements
Abstract
Purpose: We present a methodological overview of a respiration chamber at the Experimental and Clinical Research Center in Berlin, Germany. Since 2010, we investigated 750 healthy subjects and patients with various diseases. We routinely measure resting energy expenditure (REE), dietary-induced thermogenesis, and activity energy expenditure.
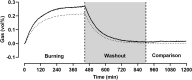
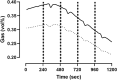
Methods: The chamber is a pull calorimeter with a total volume of 11,000 L. The majority of measurements is done with a flow rate of 120 L/min, yielding a favorable time constant of 1.53 h. The gas analysis system consists of two paramagnetic O2 sensors and two infrared CO2 sensors, one for incoming and one for outgoing air samples. O2 and CO2 sensors are calibrated simultaneously before each measurement with a 6 min calibration routine. To verify the accuracy of the whole the calorimetric system, it is validated every 2 weeks by 2 h acetone burning tests.
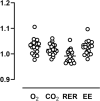
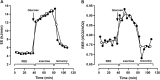
Results: Validation factors (calculated/measured) of 20 representative 2 h acetone burning tests were 1.03 ± 0.03 for [Formula: see text], 1.02 ± 0.02 for [Formula: see text], 0.99 ± 0.02 for RER, and 1.03 ± 0.03 for EE. Four repeated 60 min REE measurements of a healthy woman showed variabilities of 231.9 ± 4.8 ml/min for [Formula: see text] (CV 2.1%), 166.0 ± 6.3 ml/min for [Formula: see text] (CV 3.8%), 0.73 ± 0.03 for RER (CV 4.6%), and 4.55 ± 0.07 kJ/min for EE (CV 1.6%).
Conclusions: The data presented show that our respiration chamber produces precise and valid EE measurements with an exceptionally fast responsiveness.
Keywords: Diet-induced thermogenesis; Energy expenditure; Respiration chamber; Whole-room calorimeter.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures

References
-
- Atwater WO, Benedict FG. A respiration calorimeter with appliance for direct determination of oxygen. Washington: Carnegie Inst. of Washington; 1905.
-
- Chen KY, Smith S, Ravussin E, Krakoff J, Plasqui G, Tanaka S, Murgatroyd P, Brychta R, Bock C, Carnero E, Schoffelen P, Hatamoto Y, Rynders C, Melanson EL. Room indirect calorimetry operating and reporting standards (RICORS 1.0): a guide to conducting and reporting human whole-room calorimeter studies. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2020;28(9):1613–1625. doi: 10.1002/oby.22928. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

