Modulation of amygdala activity for emotional faces due to botulinum toxin type A injections that prevent frowning
- PMID: 36849797
- PMCID: PMC9971043
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-29280-x
Modulation of amygdala activity for emotional faces due to botulinum toxin type A injections that prevent frowning
Abstract
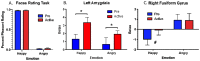
According to the facial feedback hypothesis, when we see an angry or happy face, we contract or flex the relevant muscles to recreate the expression to assist in identifying and experiencing the emotion reflected. We investigated the facial feedback hypothesis by using botulinum toxin type A (onabotulinumtoxinA; onabotA) injections to induce temporary paralysis in the glabellar muscles (responsible for frowning) and measured functional brain activity during the processing of emotional faces. Ten females viewed pictures of happy and angry faces during two functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scan sessions: one prior (Pre) to onabotA and one following (Active) onabotA injections. We found Pre vs. Active onabotA modulation of activity in the amygdala for both happy and angry faces, as well as modulation of activity in the fusiform gyrus for happy faces. Consistent with our predictions, preventing frowning through inhibition of glabellar muscle contraction altered amygdala processing for emotional faces. The modulation of amygdala and fusiform gyrus activity following onabotA may reflect compensatory processes in a neuroanatomical circuit involved in emotional processing that is engaged when facial feedback is impaired. These data contribute to a growing literature suggesting that inhibition of glabellar muscle contraction alters neural activity for emotional processing.Clinical Trials.gov registration number: NCT03373162.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This study was sponsored by a grant from Allergan, an AbbVie Company (grant number ITT-00972), awarded to Dr. Craig Stark. Dr. Mitchell Brin, an author on this study, is an employee of AbbVie, and receives stock or stock options in AbbVie. The other authors have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Paradoxical Prefrontal-Amygdala Recruitment to Angry and Happy Expressions in Pediatric Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Nov;41(12):2903-2912. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.104. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27329685 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin-induced facial muscle paralysis affects amygdala responses to the perception of emotional expressions: preliminary findings from an A-B-A design.Biol Mood Anxiety Disord. 2014 Oct 31;4:11. doi: 10.1186/2045-5380-4-11. eCollection 2014. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord. 2014. PMID: 25694806 Free PMC article.
-
Amygdala hyperactivation to angry faces in intermittent explosive disorder.J Psychiatr Res. 2016 Aug;79:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 24. J Psychiatr Res. 2016. PMID: 27145325
-
Functional atlas of emotional faces processing: a voxel-based meta-analysis of 105 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009 Nov;34(6):418-32. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19949718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Face of Emotion: Botulinum Toxin, Emotional Anatomy, and Mood Modulation.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jun;24(6):e70264. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70264. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40421911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA) mechanism of action.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 1;102(S1):e32372. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032372. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37499078 Free PMC article.
-
A simple psychophysical procedure separates representational and noise components in impairments of speech prosody perception after right-hemisphere stroke.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64295-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956187 Free PMC article.
-
The pluripotential evolution and journey of Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA).Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 1;102(S1):e32373. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032373. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37499079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum Toxin Injections for Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Trial Landscape.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Apr 15;16(4):191. doi: 10.3390/toxins16040191. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668616 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between blepharospasm and psychological diseases: the anxiety, depression and sleep disorder study.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Nov 18;17(11):2007-2013. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.11.05. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39559314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jäncke L. Facial EMG in an anger-provoking situation: individual differences in directing anger outwards or inwards. Int. J. Psychophysiol. Off. J. Int. Organ. Psychophysiol. 1996;23:207–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

