Reconstructing B cell lineage trees with minimum spanning tree and genotype abundances
- PMID: 36849917
- PMCID: PMC9972711
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-022-05112-z
Reconstructing B cell lineage trees with minimum spanning tree and genotype abundances
Abstract
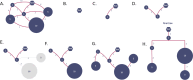
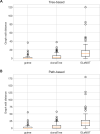
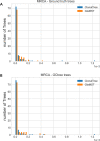
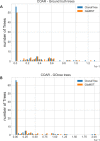
B cell receptor (BCR) genes exposed to an antigen undergo somatic hypermutations and Darwinian antigen selection, generating a large BCR-antibody diversity. This process, known as B cell affinity maturation, increases antibody affinity, forming a specific B cell lineage that includes the unmutated ancestor and mutated variants. In a B cell lineage, cells with a higher antigen affinity will undergo clonal expansion, while those with a lower affinity will not proliferate and probably be eliminated. Therefore, cellular (genotype) abundance provides a valuable perspective on the ongoing evolutionary process. Phylogenetic tree inference is often used to reconstruct B cell lineage trees and represents the evolutionary dynamic of BCR affinity maturation. However, such methods should process B-cell population data derived from experimental sampling that might contain different cellular abundances. There are a few phylogenetic methods for tracing the evolutionary events occurring in B cell lineages; best-performing solutions are time-demanding and restricted to analysing a reduced number of sequences, while time-efficient methods do not consider cellular abundances. We propose ClonalTree, a low-complexity and accurate approach to construct B-cell lineage trees that incorporates genotype abundances into minimum spanning tree (MST) algorithms. Using both simulated and experimental data, we demonstrate that ClonalTree outperforms MST-based algorithms and achieves a comparable performance to a method that explores tree-generating space exhaustively. Furthermore, ClonalTree has a lower running time, being more convenient for building B-cell lineage trees from high-throughput BCR sequencing data, mainly in biomedical applications, where a lower computational time is appreciable. It is hundreds to thousands of times faster than exhaustive approaches, enabling the analysis of a large set of sequences within minutes or seconds and without loss of accuracy. The source code is freely available at github.com/julibinho/ClonalTree.
Keywords: B cell receptor repertoire; Lineage Tree; phylogenetics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AffMB: affinity maturation analysis with SHM-guided B-cell lineage trees.Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 1;41(7):btaf346. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf346. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40674579 Free PMC article.
-
Using B cell receptor lineage structures to predict affinity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Nov 11;16(11):e1008391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008391. eCollection 2020 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 33175831 Free PMC article.
-
Isotype-aware inference of B cell clonal lineage trees from single-cell sequencing data.Cell Genom. 2024 Sep 11;4(9):100637. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100637. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 39208795 Free PMC article.
-
The Diversity and Molecular Evolution of B-Cell Receptors during Infection.Mol Biol Evol. 2016 May;33(5):1147-57. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw015. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Mol Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 26802217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How repertoire data are changing antibody science.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 17;295(29):9823-9837. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.010181. Epub 2020 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32409582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protocol for fast clonal family inference and analysis from large-scale B cell receptor repertoire sequencing data.STAR Protoc. 2024 Jun 21;5(2):102969. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.102969. Epub 2024 Mar 18. STAR Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38502687 Free PMC article.
-
ViCloD, an interactive web tool for visualizing B cell repertoires and analyzing intraclonal diversities: application to human B-cell tumors.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Jun 28;5(2):lqad064. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad064. eCollection 2023 Jun. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37388820 Free PMC article.
-
New generalized metric based on branch length distance to compare B cell lineage trees.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 5;19(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13015-024-00267-1. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39369262 Free PMC article.
-
TRIBAL: Tree Inference of B cell Clonal Lineages.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 27:2023.11.27.568874. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.27.568874. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Genom. 2024 Sep 11;4(9):100637. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100637. PMID: 38076836 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
B cell tolerance and autoimmunity: Lessons from repertoires.J Exp Med. 2024 Sep 2;221(9):e20231314. doi: 10.1084/jem.20231314. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39093312 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Safonova Y, Pevzner PA. Igevolution: clonal analysis of antibody repertoires. bioRxiv, 2019;725424
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

