DEPDC1 and KIF4A synergistically inhibit the malignant biological behavior of osteosarcoma cells through Hippo signaling pathway
- PMID: 36849972
- PMCID: PMC9972622
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-03572-4
DEPDC1 and KIF4A synergistically inhibit the malignant biological behavior of osteosarcoma cells through Hippo signaling pathway
Abstract
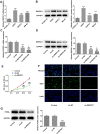
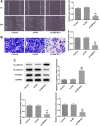
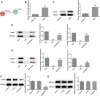
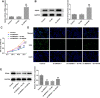
The treatment of osteosarcoma (OS) is still mainly surgery combined with systematic chemotherapy, and gene therapy is expected to improve the survival rate of patients. This study aimed to explore the effect of DEP domain 1 protein (DEPDC1) and kinesin super-family protein 4A (KIF4A) in OS and understand its mechanism. Th expression of DEPDC1 and KIF4A in OS cells was detected by RT-PCR and western blot. The viability, proliferation, invasion and migration of OS cells and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) after indicated treatment were in turn detected by CCK-8 assay, EdU staining, wound healing assay, transwell assay and tube formation assay. The interaction between DEPDC1 and KIF4A was predicted by STRING and confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation. The expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins, tube formation-related proteins and Hippo signaling pathway proteins was detected by western blot. As a result, the expression of DEPDC1 and KIF4A was all increased in U2OS cells. Down-regulation of DEPDC1 suppressed the viability, proliferation, invasion and migration of U2OS cells and tube formation of HUVECs, accompanied by the increased expression of E-cadherin and decreased expression of N-cadherin, Vimentin and VEGF. DEPDC1 was confirmed to be interacted with KIF4A. Upregulation of KIF4A partially reversed the effect of DEPDC1 interference on the above biological behaviors of U2OS cells. Down-regulation of DEPDC1 promoted the expression of p-LATS1 and p-YAP in Hippo signaling pathway, which was reversed by upregulation of KIF4A. In conclusion, down-regulation of DEPDC1 inhibited the malignant biological behavior of OS cells through the activation of Hippo signaling pathway, which could be reversed by upregulation of KIF4A.
Keywords: DEPDC1; Hippo signaling pathway; KIF4A; Osteosarcoma cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Cepeda M, Sosa AJ, Mora G. Telangiectatic osteosarcoma in an infant. Boletin medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico. 2017;74:60–64. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Geller DS, Gorlick R. Osteosarcoma: a review of diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol: H&O. 2010;8:705–718. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

