Influence of Methacrylate and Vinyl Monomers on Radical Bulk Photopolymerization Process and Properties of Epoxy-Acrylate Structural Adhesives
- PMID: 36850210
- PMCID: PMC9963875
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15040926
Influence of Methacrylate and Vinyl Monomers on Radical Bulk Photopolymerization Process and Properties of Epoxy-Acrylate Structural Adhesives
Abstract
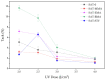
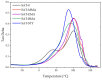
In this paper, epoxy-acrylate structural adhesives tapes (SATs) were obtained from Bisphenol A-based liquid epoxy resin and epoxy acrylic resins (EARs). A new method of EARs preparation, i.e., the free radical bulk photopolymerization process (FRBP), was studied in detail. The influence of methacrylic monomers (methyl methacrylate, ethyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate, lauryl methacrylate, (2-acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate) and vinyl monomers (N-vinylpyrrolidone and styrene) on the FRBP process of base monomers (i.e., butyl acrylate, glycidyl methacrylate and 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate) was investigated. The kinetics of photopolymerization process was monitored by photo-differential scanning calorimetry method. The properties of the obtained EARs (viscosity and average molecular weights), as well as monomers conversion using 1H NMR, were determined. It was revealed that styrene significantly decreases the photopolymerization rate and increases the final monomers conversion (+27%). However, the resulting tetrapolymers BA-co-GMA-co-HEA-co-STY have low molecular weights and low polydispersity (2.2). Methacrylate monomers with shorter aliphatic chains (<C4) also decrease the rate of photopolymerization due to the length of the aliphatic chain increasing. Surprisingly, the best results of adhesion to steel and shear strength were obtained for SAT based on epoxy acrylate resin with styrene (11 N/25 mm and 20.8 MPa, respectively). However, the thermomechanical properties of SAT with styrene were weaker than those with methacrylates.
Keywords: adhesion; epoxy acrylates; photopolymerization; polymer synthesis; structural adhesives; thermal analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Pascault J.P., Williams R.J. Epoxy Polymers: New Materials and Innovations. Wiley-VCH VerabH; New York, NY, USA: 2010.
-
- Dhole G.S., Gunasekaran G., Ghorpade T., Vinjamur M. Smart acrylic coatings for corrosion detection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017;110:140–149. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2017.04.048. - DOI
-
- Paz E., Narbón J.J., Abenojar J., Cledera M., Del Real J.C. Influence of Acrylic Adhesive Viscosity and Surface Roughness on the Properties of Adhesive Joint. J. Adhes. 2016;92:877–891.
-
- Sharma B., Sauraj S., Kumar B., Pandey A., Dutt D., Negi S.Y., Maji P.K., Kulshreshtha A. Synthesis of waterborne acrylic copolymer resin as a binding agent for the development of water-based inks in the printing application. Polym. Eng. 2021;61:1569–1580. doi: 10.1002/pen.25681. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

