New Cognitive Deep-Learning CAPTCHA
- PMID: 36850935
- PMCID: PMC9965441
- DOI: 10.3390/s23042338
New Cognitive Deep-Learning CAPTCHA
Abstract
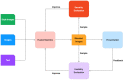
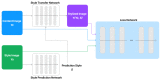
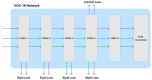
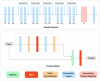
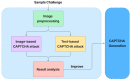
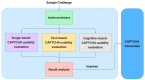
CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), or HIP (Human Interactive Proof), has long been utilized to avoid bots manipulating web services. Over the years, various CAPTCHAs have been presented, primarily to enhance security and usability against new bots and cybercriminals carrying out destructive actions. Nevertheless, automated attacks supported by ML (Machine Learning), CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), and DNN (Deep Neural Network) have successfully broken all common conventional schemes, including text- and image-based CAPTCHAs. CNN/DNN have recently been shown to be extremely vulnerable to adversarial examples, which can consistently deceive neural networks by introducing noise that humans are incapable of detecting. In this study, the authors improve the security for CAPTCHA design by combining text-based, image-based, and cognitive CAPTCHA characteristics and applying adversarial examples and neural style transfer. Comprehend usability and security assessments are performed to evaluate the efficacy of the improvement in CAPTCHA. The results show that the proposed CAPTCHA outperforms standard CAPTCHAs in terms of security while remaining usable. Our work makes two major contributions: first, we show that the combination of deep learning and cognition can significantly improve the security of image-based and text-based CAPTCHAs; and second, we suggest a promising direction for designing CAPTCHAs with the concept of the proposed CAPTCHA.
Keywords: CAPTCHA; cognitive; deep learning; security.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Inayat U., Zia M.F., Mahmood S., Khalid H.M., Benbouzid M. Learning-Based Methods for Cyber Attacks Detection in IoT Systems: A Survey on Methods, Analysis, and Future Prospects. Electronics. 2022;11:1502. doi: 10.3390/electronics11091502. - DOI
-
- von Ahn L., Blum M., Hopper N.J., Langford J. Eurocrypt. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2003. CAPTCHA: Using Hard AI Problems for Security.
-
- Szegedy C., Zaremba W., Sutskever I., Bruna J., Erhan D., Goodfellow I.J., Fergus R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv. 20131312.6199
-
- Gatys L., Ecker A., Bethge M. A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style. arXiv. 2015 doi: 10.1167/16.12.326.1508.06576 - DOI
-
- Gao H., Tang M., Liu Y., Zhang P., Liu X. Research on the Security of Microsoft’s Two-Layer Captcha. IEEE Trans. Inf. Secur. 2017;12:1671–1685. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2682704. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

