Ex Vivo Blockade of the PD-1 Pathway Improves Recall IFNγ Responses of HIV-Infected Persons on Antiretroviral Therapy
- PMID: 36851089
- PMCID: PMC9965969
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11020211
Ex Vivo Blockade of the PD-1 Pathway Improves Recall IFNγ Responses of HIV-Infected Persons on Antiretroviral Therapy
Abstract
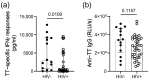
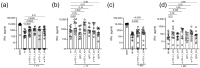
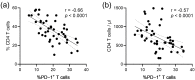
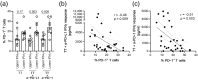
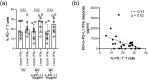
Despite antiretroviral therapy (ART), immune exhaustion persists in HIV infection and limits T cell responses to HIV or other pathogens. Moreover, HIV infection results in the loss of pre-existing immunity. Here, we investigated the effect of blocking the PD-1 pathway on recall IFNγ responses to tetanus toxoid (TT) and measles virus (MV) antigens in HIV-infected persons on ART with prior TT and MV immunity. The ex vivo treatment of lymphocytes with anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies significantly increased TT- and MV-specific IFNγ responses. The responses to TT and MV antigens alone or in combination with antibodies blocking the PD-1 pathway positively correlated with CD4 T cell levels. Furthermore, T cell PD-1 expression levels inversely correlated with recall IFNγ responses in combination with antibodies blocking the PD-1 pathway but not with IFNγ responses to antigens only. Our study suggested that targeting the PD-1 pathway may boost vaccine-induced pre-existing immunity in HIV-infected persons on ART depending on the degree of immune exhaustion.
Keywords: HIV infection; PD-1 pathway; T cell exhaustion; anti-PD-1; anti-PD-L1; vaccine-induced immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- D’Souza M., Fontenot A.P., Mack D.G., Lozupone C., Dillon S., Meditz A., Wilson C.C., Connick E., Palmer B.E. Programmed Death 1 Expression on Hiv-Specific Cd4+ T Cells Is Driven by Viral Replication and Associated with T Cell Dysfunction. J. Immunol. 2007;179:1979–1987. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1979. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Day C.L., Kaufmann D.E., Kiepiela P., Brown J.A., Moodley E.S., Reddy S., Mackey E.W., Miller J.D., Leslie A.J., DePierres C., et al. Pd-1 Expression on Hiv-Specific T Cells Is Associated with T-Cell Exhaustion and Disease Progression. Nature. 2006;443:350–354. doi: 10.1038/nature05115. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

