Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion
- PMID: 36851100
- PMCID: PMC9965342
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11020220
Blood Transfusion Components Inducing Severe Allergic Reactions: The First Case of Kounis Syndrome Induced by Platelet Transfusion
Abstract
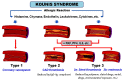
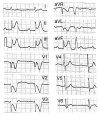
Kounis syndrome is a multisystem and multidisciplinary disease affecting the circulatory system that can be manifested as spasm and thrombosis. It can occur as allergic, hypersensitivity, anaphylactic, or anaphylactoid reactions associated with the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells and from other interrelated and interacting inflammatory cells, including macrophages and lymphocytes. A platelet subset with high- and low-affinity IgE surface receptors is also involved in this process. Whereas the heart, and particularly the coronary arteries, constitute the primary targets of inflammatory mediators, the mesenteric, cerebral, and peripheral arteries are also vulnerable. Kounis syndrome is caused by a variety of factors, including drugs, foods, environmental exposure, clinical conditions, stent implantation, and vaccines. We report a unique case of a 60-year-old male with a past medical history of allergy to human albumin, alcoholic cirrhosis, and esophageal varices, who was admitted due to multiple episodes of hematemesis. Due to low hemoglobin levels, he was transfused with 3 units of red blood cells and fresh frozen plasma without any adverse reactions. On the third day of hospitalization, severe thrombocytopenia was observed and transfusion of platelets was initiated. Immediately following platelet infusion, the patient developed chest discomfort, skin signs of severe allergic reaction, and hemodynamic instability. The electrocardiogram revealed ST segment elevation in the inferior leads. Given the strong suspicion of Kounis syndrome/allergic coronary spasm, the patient was treated with anti-allergic treatment only, without any anti-platelet therapy. The clinical status of the patient gradually improved and the electrocardiographic changes reverted to normal. Based on these findings, Kounis hypersensitivity-associated acute coronary syndrome, specifically, type I Kounis syndrome, was diagnosed. Although platelet transfusion can be a life-saving therapy, each blood transfusion carries a substantial risk of adverse reactions. The aims of this report are to expand the existing knowledge of patient responses to blood transfusion and provide information on the incidence of various severe transfusion reactions to all blood components and especially to platelets. To the best of our knowledge, Kounis syndrome induced by platelet transfusionhas never been previously reported. Hypersensitivity to platelet external membrane glycoproteins in an atopic patient seems to be the possible etiology. Despite that Kounis syndrome remains an under-diagnosed clinical entity in everyday practice, it should always be considered in the differential diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes.
Keywords: Kounis syndrome; allergy; anaphylaxis; blood components; blood transfusion; platelets; transfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the case report was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kounis Syndrome—not a Single-organ Arterial Disorder but a Multisystem and Multidisciplinary Disease.Balkan Med J. 2019 Jul 11;36(4):212-221. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2019.2019.5.62. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Balkan Med J. 2019. PMID: 31198019 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary hypersensitivity disorder: the Kounis syndrome.Clin Ther. 2013 May;35(5):563-71. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.02.022. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Clin Ther. 2013. PMID: 23490289 Review.
-
Kounis syndrome: a new twist on an old disease.Future Cardiol. 2011 Nov;7(6):805-24. doi: 10.2217/fca.11.63. Future Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 22050066 Review.
-
The more allergens an atopic patient is exposed to, the easier and quicker anaphylactic shock and Kounis syndrome appear: Clinical and therapeutic paradoxes.J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2014 Jul;5(2):240-4. doi: 10.4103/0976-9668.136145. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 25097390 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent cardiac arrests caused by Kounis syndrome without typical allergic symptoms.J Cardiol Cases. 2022 Oct 28;27(2):47-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2022.10.004. eCollection 2023 Feb. J Cardiol Cases. 2022. PMID: 36788958 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kounis syndrome type I induced by an intramuscular injection of diclofenac: A literature review based on a case report.Clin Case Rep. 2024 Jul 21;12(7):e9198. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.9198. eCollection 2024 Jul. Clin Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39040609 Free PMC article.
-
IgE sensitization profiles to food, inhalant and insect venom in Norwegian blood donors and their impact on blood transfusions.Scand J Immunol. 2025 Jan;101(1):e13425. doi: 10.1111/sji.13425. Scand J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39648460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shadaksharappa K.S., Pillai H.K., Mohan N.T., Chandrasekhra Rao A.S. Myocardial infarction following blood transfusion. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1963;40:378–380. - PubMed
-
- Kondo Y., Nomura M., Nada T., Endo J., Yukinaka M., Saito K., Ichikawa S., Ito S., Nakaya Y. Ischaemic electrocardiographic changes after massive blood transfusion: Findings based on myocardial scintigraphy using 99mTc-MIBI and 123I-MIBG. Acta Cardiol. 1998;53:279–283. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

