Adenovirus Vaccine Containing Truncated SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Subunit Leads to a Specific Immune Response in Mice
- PMID: 36851306
- PMCID: PMC9968167
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11020429
Adenovirus Vaccine Containing Truncated SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Subunit Leads to a Specific Immune Response in Mice
Abstract
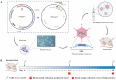
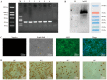
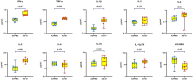
The development of an efficient and safe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine is a crucial approach for managing the severe acute respiratory disease coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic in light of current conditions. In this study, we produced a shortened segment of the optimized SARS-CoV-2 spike gene (2043 bp, termed S1) that was able to encode a truncated S1 protein. The protein was tested to determine if it could elicit efficient immunization in mice against SARS-CoV-2. The presence of the S1 protein was confirmed with immunofluorescence and Western blotting. An adenovirus vaccine bearing the S1 gene fragment (Ad-S1) was administered intramuscularly to mice four times over 4 weeks. SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein humoral immunity was demonstrated in all immunized mice. The serum from immunized mice demonstrated excellent anti-infection activity in vitro. A robust humoral immune response against SARS-CoV-2 was observed in the mice after vaccination with Ad-S1, suggesting that the adenovirus vaccine may aid the development of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and other genetically distinct viruses.
Keywords: S1 gene; SARS-CoV-2; adenoviral vector; immunity; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Trougakos I.P., Stamatelopoulos K., Terpos E., Tsitsilonis O.E., Aivalioti E., Paraskevis D., Kastritis E., Pavlakis G.N., Dimopoulos M.A. Insights to SARS-CoV-2 life cycle, pathophysiology, and rationalized treatments that target COVID-19 clinical complications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021;28:9. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00703-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

