Cardiac Arrhythmias in Post-COVID Syndrome: Prevalence, Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- PMID: 36851603
- PMCID: PMC9959721
- DOI: 10.3390/v15020389
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Post-COVID Syndrome: Prevalence, Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Abstract
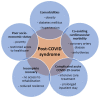
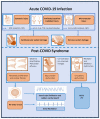
An increase in post-COVID patients with late sequelae of acute COVID-19 infection is emerging as an ongoing challenge for physicians and healthcare professionals. Since the beginning of the pandemic, it has rapidly become evident that the acute infection is not limited to the respiratory tract but that several organs, including the cardiovascular system, can be affected. Moreover, in a significant proportion of patients (ranging from about 10 to up to 50%) with former COVID-19, cardiopulmonary symptoms such as dyspnea, palpitations, restricted physical capacity, and cardiac arrhythmias can persist weeks and months after the acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. The spectrum of COVID-19-associated arrhythmias is rather wide, most likely due to various pathomechanisms. In this article, the prevalence of cardiac arrhythmias and underlying pathologies are reviewed, including direct myocardial injury and abnormal consequences with an impact on cardiac electric instability. The hyperinflammatory reaction of the host immune system is specifically considered. Moreover, several distinct rhythm disorders occurring in post-COVID patients are discussed with regard to their clinical management.
Keywords: cardiac arrhythmias and channelopathies; cytokines; myocardial injury; post-COVID syndrome; systemic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Garrigues E., Janvier P., Kherabi Y., Le Bot A., Hamon A., Gouze H., Doucet L., Berkani S., Oliosi E., Mallart E., et al. Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020;81:e4–e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

