Longitudinal IgA and IgG Response, and ACE2 Binding Blockade, to Full-Length SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variants in a Population of Black PLWH Vaccinated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
- PMID: 36851662
- PMCID: PMC9965153
- DOI: 10.3390/v15020448
Longitudinal IgA and IgG Response, and ACE2 Binding Blockade, to Full-Length SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variants in a Population of Black PLWH Vaccinated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
Abstract
Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 have been pivotal in overcoming the COVID-19 pandemic yet understanding the subsequent outcomes and immunological effects remain crucial, especially for at-risk groups e.g., people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (PLWH). In this study we report the longitudinal IgA and IgG antibody titers, as well as antibody-mediated angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binding blockade, against the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) proteins after 1 and 2 doses of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine in a population of Black PLWH. Here, we report that PLWH (N = 103) did not produce an anti-S IgA response after infection or vaccination, however, anti-S IgG was detected in response to vaccination and infection, with the highest level detected for infected vaccinated participants. The anti-IgG and ACE2 blockade assays revealed that both vaccination and infection resulted in IgG production, however, only vaccination resulted in a moderate increase in ACE2 binding blockade to the ancestral S protein. Vaccination with a previous infection results in the greatest anti-S IgG and ACE2 blockade for the ancestral S protein. In conclusion, PLWH produce an anti-S IgG response to the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine and/or infection, and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination with a previous infection produced more neutralizing antibodies than vaccination alone.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04444674.
Keywords: COVID-19; HIV; IgA; IgG; SARS-CoV-2 spike protein; neutralization; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
J.M.B. is an employee of Sengenics Corporation, who market a Protein Array product developed in part based on results generated in this study. That product was however not used in this study.
Figures
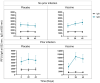
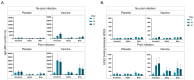

References
-
- Tegally H., Wilkinson E., Giovanetti M., Iranzadeh A., Fonseca V., Giandhari J., Doolabh D., Pillay S., San E.J., Msomi N., et al. Emergence and Rapid Spread of a New Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Lineage with Multiple Spike Mutations in South Africa. Epidemiology. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.12.21.20248640. - DOI
-
- Madhi S.A., Koen A.L., Izu A., Fairlie L., Cutland C.L., Baillie V., Padayachee S.D., Dheda K., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 (AZD1222) Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in People Living with and without HIV in South Africa: An Interim Analysis of a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1B/2A Trial. Lancet HIV. 2021;8:e568–e580. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00157-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

