Investigating the effect of vaccinated population on the COVID-19 prediction using FA and ABC-based feed-forward neural networks
- PMID: 36852029
- PMCID: PMC9958458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13672
Investigating the effect of vaccinated population on the COVID-19 prediction using FA and ABC-based feed-forward neural networks
Abstract
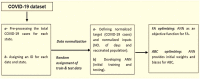
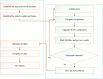
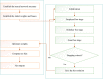
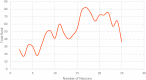
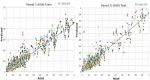
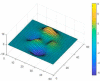
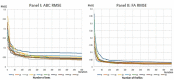
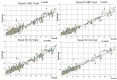
Since 2019, the coronavirus outbreak has caused many catastrophic events all over the world. At the current time, the massive vaccination has been considered as the most efficient way to fight against the pandemic. This study schemes to explain and model COVID-19 cases by considering the vaccination rate. We utilized an amalgamation of neural network (NN) with two powerful optimization algorithms, i.e., firefly algorithm and artificial bee colony. For validating the models, we employed the COVID-19 datasets regarding the vaccination rate and the total confirmed cases for 51 states since the beginning of vaccination in the US. The numerical experiment indicated that by considering the vaccinated population, the accuracy of NN increases exponentially when compared with the same NN in the absence of the vaccinated population. During the next stage, the NN with vaccinated input data is elected for firefly and bee optimizing. Based upon the firefly optimizing, 93.75% of COVID-19 cases can be explained in all states. According to the bee optimizing, 92.3% of COVID-19 cases is explained since the massive vaccination. Overall, it can be concluded that the massive vaccination is the key predictor of COVID-19 cases on a grand scale.
Keywords: COVID-19; Forecasting; Modeling; Neural networks; Vaccinated population.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of robustness of hybrid artificial neural network with artificial bee colony and firefly algorithm in predicting COVID-19 new cases: case study of Iran.Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. 2022;36(9):2461-2476. doi: 10.1007/s00477-021-02098-7. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. 2022. PMID: 34608374 Free PMC article.
-
An innovative ensemble model based on multiple neural networks and a novel heuristic optimization algorithm for COVID-19 forecasting.Expert Syst Appl. 2023 Feb;212:118746. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118746. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Expert Syst Appl. 2023. PMID: 36089985 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Breast Cancer Diagnosis Scheme With Intelligent Feature and Parameter Selections.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Feb;214:106432. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106432. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 34844767
-
A COVID-19 Pandemic Artificial Intelligence-Based System With Deep Learning Forecasting and Automatic Statistical Data Acquisition: Development and Implementation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 May 20;23(5):e27806. doi: 10.2196/27806. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33900932 Free PMC article.
-
The Burden of Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Cases, Hospitalizations, and Mortality Based on Vaccination Status and Mandated Mask Use: Statewide Data From Wisconsin and Narrative Review of the Literature.Anesth Analg. 2022 Mar 1;134(3):524-531. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005858. Anesth Analg. 2022. PMID: 35180169 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical Impedance Tomography of Industrial Two-Phase Flow Based on Radial Basis Function Neural Network Optimized by the Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 4;23(17):7645. doi: 10.3390/s23177645. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37688101 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of COVID-19 vaccination on human mobility: The London case.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 4;9(8):e18769. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18769. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37636432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- (WHO) W.H.O. 2021. WHO-Convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part.
-
- Cascella M., et al. 2022. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Statpearls [internet] - PubMed
-
- (WHO) W.H.O. November 2021. COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

