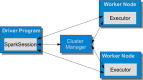
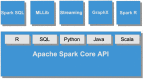
Framing Apache Spark in life sciences
- PMID: 36852030
- PMCID: PMC9958288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13368
Framing Apache Spark in life sciences
Abstract
Advances in high-throughput and digital technologies have required the adoption of big data for handling complex tasks in life sciences. However, the drift to big data led researchers to face technical and infrastructural challenges for storing, sharing, and analysing them. In fact, this kind of tasks requires distributed computing systems and algorithms able to ensure efficient processing. Cutting edge distributed programming frameworks allow to implement flexible algorithms able to adapt the computation to the data over on-premise HPC clusters or cloud architectures. In this context, Apache Spark is a very powerful HPC engine for large-scale data processing on clusters. Also thanks to specialised libraries for working with structured and relational data, it allows to support machine learning, graph-based computation, and stream processing. This review article is aimed at helping life sciences researchers to ascertain the features of Apache Spark and to assess whether it can be successfully used in their research activities.
Keywords: 00-01; 99-00; Apache Spark; Big data; HPC; Parallel computing.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Big Data in metagenomics: Apache Spark vs MPI.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 6;15(10):e0239741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239741. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33022000 Free PMC article.
-
A distributed computing model for big data anonymization in the networks.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 28;18(4):e0285212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285212. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37115783 Free PMC article.
-
Big Data Approaches for the Analysis of Large-Scale fMRI Data Using Apache Spark and GPU Processing: A Demonstration on Resting-State fMRI Data from the Human Connectome Project.Front Neurosci. 2016 Jan 6;9:492. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00492. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26778951 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics applications on Apache Spark.Gigascience. 2018 Aug 1;7(8):giy098. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy098. Gigascience. 2018. PMID: 30101283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edge, Fog, and Cloud Against Disease: The Potential of High-Performance Cloud Computing for Pharma Drug Discovery.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2716:181-202. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3449-3_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37702940 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and technologies in cancer epigenetics.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 7;14:1513654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1513654. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39839798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- https://www.embl.org/files/wp-content/uploads/EMBL-EBI_Annual-Report_202... Embl-ebi annual report 2020. URL.
-
- Unravelling the Human Genome–Phenome Relationship Using Phenome-Wide Association StudiesNat. Rev. Genet. 2016;17:129–145. - PubMed
-
- Atasoy H., Greenwood B.N., McCullough J.S. 2019. The digitization of patient care: a review of the effects of electronic health records on health care quality and utilization. Tech. Rep. - PubMed
-
- Zhou L., Pan S., Wang J., Vasilakos A. Machine learning on big data: opportunities and challenges. Neurocomputing. 2017;237:350–361. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.026. - DOI
-
- Parliament, Eurpean Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation) Off. J. Eur. Union. 2016;119(1)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources