Thermoactive metallo-keratinase from Bacillus sp. NFH5: Characterization, structural elucidation, and potential application as detergent additive
- PMID: 36852054
- PMCID: PMC9957710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13635
Thermoactive metallo-keratinase from Bacillus sp. NFH5: Characterization, structural elucidation, and potential application as detergent additive
Abstract
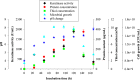
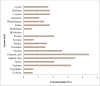
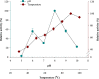
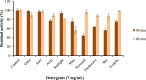
In recent times, robust green technological developments have advanced the goal of a circular economy by minimizing waste generation. The study was undertaken to explore the keratinolytic activity of chicken feather-degrading bacteria from South African soil. Isolates coded as SSN-01 and HSN-01 were identified as Bacillus sp. NFH5 and Bacillus sp. FHNM and their sequences were deposited in GenBank, with accession numbers MW165830.1 and MW165831.1, respectively. Extracellular enzyme production and thiol group generation by Bacillus sp. NFH5 peaked at 120 h with 1879.09 ± 88.70 U/mL and 9.49 ± 0.78 mM, respectively. Glutamic acid (4.44%), aspartic acid (3.50%), arginine (3.23%), glycine (2.61%), serine (2.08%), and proline (2.08%) were relatively higher in concentration. Keratinase (KerBAN) activity was highest at pH 8.0 and 90 °C but was inhibited by both EDTA and 1,10-phenanthroline. In addition, the keratinase-encoding gene (kerBAN) accessioned OK033360 had 362 amino acid residues, with molecular weight and theoretical isoelectric point of 39 kDa and 8.81, respectively. Findings from this study highlight the significance of Bacillus sp. NFH5 in the bio-recycling of recalcitrant keratinous wastes to protein hydrolysates - potential dietary supplements for livestock feeds. The properties of KerBAN underscore its application potential in green biotechnological processes.
Keywords: Amino acids; Bio-recycling; Keratinolytic protease; Livestock feed; Protein hydrolysate.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chryseobacterium aquifrigidense keratinase liberated essential and nonessential amino acids from chicken feather degradation.Environ Technol. 2023 Jan;44(3):293-303. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2021.1969597. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Environ Technol. 2023. PMID: 34397312
-
Biochemical and Molecular Characterization of a Thermostable Alkaline Metallo-Keratinase from Bacillus sp. Nnolim-K1.Microorganisms. 2020 Aug 27;8(9):1304. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091304. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32867042 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable production, biochemical and molecular characterization of thermo-and-solvent stable alkaline serine keratinase from novel Bacillus pumilus AR57 for promising poultry solid waste management.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 15;163:135-146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.219. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32615225
-
Molecular strategies to increase keratinase production in heterologous expression systems for industrial applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 May;105(10):3955-3969. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11321-y. Epub 2021 May 3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33937928 Review.
-
Microbial Keratinase: Next Generation Green Catalyst and Prospective Applications.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 18;11:580164. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.580164. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strawberry Protease as a Laundry Detergent Additive Candidate: Immobilization, Compatibility Study with Detergent Ingredients, and Washing Performance Test.Glob Chall. 2023 Nov 24;8(1):2300102. doi: 10.1002/gch2.202300102. eCollection 2024 Jan. Glob Chall. 2023. PMID: 38223888 Free PMC article.
-
High keratinase and other types of hydrolase activity of the new strain of Bacillus paralicheniformis.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 25;19(10):e0312679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312679. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39453952 Free PMC article.
-
Metal Nanomaterials and Hydrolytic Enzyme-Based Formulations for Improved Antifungal Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 12;24(14):11359. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411359. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on thermostable keratinases for protein engineering against feather pollutants.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 25;109(1):75. doi: 10.1007/s00253-025-13459-5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40131452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial purification and characterization of protease extracted from kinema.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 27;10(5):e27173. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27173. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shestakova A., Timorshina S., Osmolovskiy A. Biodegradation of keratin-rich husbandry waste as a path to sustainable agriculture. Sustainability. 2021;13:8691. doi: 10.3390/su13168691. - DOI
-
- Falade A.O. Valorization of agricultural wastes for production of biocatalysts of environmental significance: towards a sustainable environment. Environ. Sustain. 2021;4:317–328. doi: 10.1007/s42398-021-00183-9. - DOI
-
- Biswas I., Mitra D., Senapati A., Mitra D., Chattaraj S., Ali M., Basak G., Panneerselvam P., Das Mohapatra P.K. Valorization of vermicompost with bacterial fermented chicken feather hydrolysate for the yield improvement of tomato plant: a novel organic combination. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2021;10:29–42. doi: 10.30486/ijrowa.2020.1904599.1104. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

