Sofosbuvir plus velpatasvir for 8 weeks in patients with acute hepatitis C: The HepNet acute HCV-V study
- PMID: 36852107
- PMCID: PMC9957891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100650
Sofosbuvir plus velpatasvir for 8 weeks in patients with acute hepatitis C: The HepNet acute HCV-V study
Abstract
Background & aims: EASL guidelines recommend 8 weeks of treatment with sofosbuvir plus velpatasvir (SOF/VEL) for the treatment of acute or recently acquired HCV infection, but only 6- and 12-week data are available. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a shortened 8-week SOF/VEL treatment for acute HCV monoinfection.
Methods: In this investigator-initiated, prospective, multicentre, single-arm study, we recruited 20 adult patients with acute HCV monoinfection from nine centers in Germany. Patients received SOF/VEL (400/100 mg) as a fixed-dose combination tablet once daily for 8 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with sustained virological response 12 weeks after the end of treatment (SVR12).
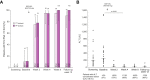
Results: The median HCV RNA viral load at baseline was 104,307 IU/ml; the distribution of HCV genotypes was as follows: GT1a/1b/2/3/4: n = 12/1/1/3/3. Thirteen (65%) of the 20 patients were taking medication for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis. SVR12 was achieved in all patients who complied with the study protocol (n = 18/18 [100%], per protocol analysis), but the primary endpoint was not met in the intention-to-treat analysis (n = 18/20 [90%]) because two patients were lost to follow-up. One serious adverse event (unrelated to study drug) occurred during 12 weeks of post-treatment follow-up.
Conclusions: The 8-week treatment with SOF/VEL was well tolerated and highly effective in all adherent patients with acute HCV monoinfection. Early treatment of hepatitis C might effectively prevent the spread of HCV in high-risk groups.
Clinical trial number: NCT03818308.
Impact and implications: The HepNet acute HCV-V study (NCT03818308), an investigator-initiated, single-arm, multicenter pilot study, demonstrates the efficacy and safety of 8 weeks of daily treatment with the fixed-dose combination sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (400/100 mg) in patients with acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. All patients who completed therapy and were followed-up achieved sustained virologic response. Thus, early treatment with SOF/VEL which might effectively prevent the spread of HCV in high-risk groups can be recommended for patients with acute HCV monoinfection.
Keywords: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HCV, hepatitis C virus; ITT, intention-to-treat; LLOQ, lower limit of quantification; PP, per protocol; SVR, sustained virologic response; ULN, upper limit of normal; acute HCV infection; direct-acting antivirals; hepatitis C elimination; recently acquired infection.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest concerning the content of this manuscript. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and safety of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir in patients with chronic hepatitis C previously treated with DAAs.J Hepatol. 2019 Oct;71(4):666-672. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31203153 Clinical Trial.
-
Ledipasvir plus sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination for 6 weeks in patients with acute hepatitis C virus genotype 1 monoinfection (HepNet Acute HCV IV): an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2017 Feb;17(2):215-222. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30408-X. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28029529 Clinical Trial.
-
Real-life effectiveness and safety of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir in hepatitis C patients with previous DAA failure.J Hepatol. 2019 Dec;71(6):1106-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.07.020. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31433303
-
Sofosbuvir plus velpatasvir combination for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients with end stage renal disease on renal replacement therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2022 Jan;27(1):82-89. doi: 10.1111/nep.13968. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Nephrology (Carlton). 2022. PMID: 34453374
-
Pharmacoeconomic Review Report: Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir (Vosevi): (Gilead Sciences Canada, Inc.): Indication: Hepatitis C infection genotype 1 to 6 [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018 Feb. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018 Feb. PMID: 30480922 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Microelimination of Hepatitis C in Thailand, Phetchabun Model: Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 3;14(11):3946. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113946. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different dynamics of soluble inflammatory mediators after clearance of respiratory SARS-CoV-2 versus blood-borne hepatitis C virus infections.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 22;14(1):29013. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79909-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39578604 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Hepatitis C: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Viruses. 2024 Nov 6;16(11):1739. doi: 10.3390/v16111739. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute hepatitis C virus infection: clinical update and remaining challenges.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Jul;29(3):623-642. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0349. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36800699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SASLT guidelines: Update in treatment of hepatitis C virus infection, 2024.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 1;30(Supp 1):S1-S42. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_333_23. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38167232 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

