Fluorescent detection of emerging virus based on nanoparticles: From synthesis to application
- PMID: 36852170
- PMCID: PMC9946731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.116999
Fluorescent detection of emerging virus based on nanoparticles: From synthesis to application
Abstract
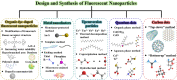
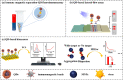
The spread of COVID-19 has caused huge economic losses and irreversible social impact. Therefore, to successfully prevent the spread of the virus and solve public health problems, it is urgent to develop detection methods with high sensitivity and accuracy. However, existing detection methods are time-consuming, rely on instruments, and require skilled operators, making rapid detection challenging to implement. Biosensors based on fluorescent nanoparticles have attracted interest in the field of detection because of their advantages, such as high sensitivity, low detection limit, and simple result readout. In this review, we systematically describe the synthesis, intrinsic advantages, and applications of organic dye-doped fluorescent nanoparticles, metal nanoclusters, up-conversion particles, quantum dots, carbon dots, and others for virus detection. Furthermore, future research initiatives are highlighted, including green production of fluorescent nanoparticles with high quantum yield, speedy signal reading by integrating with intelligent information, and error reduction by coupling with numerous fluorescent nanoparticles.
Keywords: Detection; Emerging virus; Fluorescence nanoparticles; Fluorometric sensors; Public health.
© 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Dual-Readout Method for Biothiols Detection Based on the NSET of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots-Au Nanoparticles System.J Fluoresc. 2017 Sep;27(5):1597-1605. doi: 10.1007/s10895-017-2095-1. Epub 2017 Apr 11. J Fluoresc. 2017. PMID: 28401410
-
A dual-mode nanosensor based on carbon quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for discriminative detection of glutathione in human plasma.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Jun 15;56:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.12.038. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24462829
-
Recent advances of fluorescent sensors for bacteria detection-A review.Talanta. 2023 Mar 1;254:124133. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.124133. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 36459871 Review.
-
Perspective on recent developments of nanomaterial based fluorescent sensors: Applications in safety and quality control of food and beverages.J Food Drug Anal. 2020 Dec 15;28(4):486-507. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.1270. J Food Drug Anal. 2020. PMID: 35696140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional surface engineering of C-dots for fluorescent biosensing and in vivo bioimaging.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Jan 21;47(1):20-30. doi: 10.1021/ar400023s. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 23911118 Review.
Cited by
-
Virus-like particle encapsulation of functional proteins: advances and applications.Theranostics. 2024 Nov 4;14(19):7604-7622. doi: 10.7150/thno.103127. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39659581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-based strategies for sample-to-answer monkeypox detection: current status and emerging opportunities.Nanotechnology. 2024 Nov 4;36(4):042001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad892b. Nanotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39433062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent-Nanoparticle-Impregnated Nanocomposite Polymeric Gels for Biosensing and Drug Delivery Applications.Gels. 2023 Aug 18;9(8):669. doi: 10.3390/gels9080669. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37623124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microparticle-Based Detection of Viruses.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 15;13(8):820. doi: 10.3390/bios13080820. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen: Role in Biopsy for Precision Medicine.Chem Rev. 2024 Oct 23;124(20):11242-11347. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00244. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39380213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., Guan L., Wei Y., Li H., Wu X., Xu J., Tu S., Zhang Y., Chen H., Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leligdowicz A., Fischer W.A., Uyeki T.M., Fletcher T.E., Adhikari N.K.J., Portella G., Lamontagne F., Clement C., Jacob S.T., Rubinson L., Vanderschuren A., Hajek J., Murthy S., Ferri M., Crozier I., Ibrahima E., Lamah M.-C., Schieffelin J.S., Brett-Major D., Bausch D.G., Shindo N., Chan A.K., O'Dempsey T., Mishra S., Jacobs M., Dickson S., Lyon G.M., Fowler R.A. Ebola virus disease and critical illness. Crit. Care. 2016;20 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
