Secondary syphilis in a 14-month-old girl and child-to-mother transmission
- PMID: 36852408
- PMCID: PMC9958271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2023.e01713
Secondary syphilis in a 14-month-old girl and child-to-mother transmission
Abstract
Syphilis cases in childhood are usually associated with congenital transmission. Acquired transmission is uncommon, and primarily related to sexual abuse or close contact/nursing with infected family members. We here describe a case of syphilis in a 14-month-old girl resulting from intrafamilial infection, with a subsequent transmission to her mother.
Keywords: Acquired syphilis; Child; Child-to-mother transmission; Intrafamilial infection.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

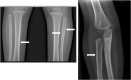
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Syphilis. Available at: 〈https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/overview.htm#Syphilis〉 [Accessed 8 July 2022].
-
- Santé Publique France. Infections sexuellement transmissibles. Available at: 〈https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/infections-... [Accessed 8 July 2022].
-
- Janier M., Unemo M., Dupin N., Tiplica G.S., Potočnik M., Patel R. 2020 European guideline on the management of syphilis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;(35):574–588. - PubMed
-
- Moscatelli G., Moroni S., García Bournissen F., et al. Acquired syphilis by nonsexual contact in childhood. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021;40:892–898. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

