Reproducibility and stability of spirometer-guided deep inspiration breath-hold in left-breast treatments using an optical surface monitoring system
- PMID: 36852489
- PMCID: PMC10243327
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13922
Reproducibility and stability of spirometer-guided deep inspiration breath-hold in left-breast treatments using an optical surface monitoring system
Abstract
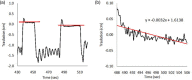
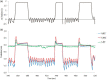
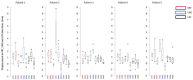
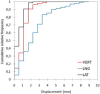
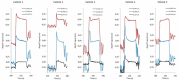
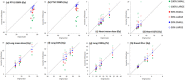
The aim of this study was to evaluate the reproducibility and stability of left breast positioning during spirometer-guided deep-inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) radiotherapy using an optical surface imaging system (AlignRT). The AlignRT optical tracking system was used to monitor five left-sided breast cancer patients treated using the Active Breathing Coordinator spirometer with DIBH technique. Treatment plans were created using an automated hybrid-VMAT technique on DIBH CTs. A prescribed dose of 60 Gy to the tumor bed and 50 Gy to the breast in 25 fractions was planned. During each treatment session, the antero-posterior (VRT), superior-inferior (LNG), and lateral (LAT) motion of patients was continuously recorded by AlignRT. The intra-breath-hold stability and the intra- and inter-fraction reproducibility were analyzed for all breath-holds and treatment fractions. The dosimetric impact of the residual motion during DIBH was evaluated from the isocenter shifts amplitudes obtained from the 50%, 90%, and 100% cumulative distribution functions of intra-fractional reproducibility. The positional variations of 590 breath-holds as measured by AlignRT were evaluated. The mean intra-breath-hold stability during DIBH was 1.0 ± 0.4 mm, 2.1 ± 1.9 mm, and 0.7 ± 0.5 mm in the VRT, LNG, and LAT directions, with a maximal value of 8.8 mm in LNG direction. Similarly, the mean intra-breath-hold reproducibility was 1.4 ± 0.8 mm, 1.7 ± 1.0 mm, and 0.8 ± 0.5 mm in the VRT, LNG, and LAT directions, with a maximal value of 4.1 mm in LNG direction. Inter-fractional reproducibility showed better reliability, with difference in breathing levels in all fractions of 0.3 mm on average. Based on tolerance limits corresponding to the 90% cumulative distribution level, gating window widths of 1 mm, 2 mm, and 5 mm in the LAT, VRT, and LNG directions were considered an appropriate choice. In conclusion, despite the use of a dedicated spirometer at constant tidal volume, a non-negligible variability of the breast surface position has been reported during breath-holds. The real-time monitoring of breast surface using surface-guided optical technology is strongly recommended.
Keywords: ABC; SGRT; VMAT; breast; breath-hold; spirometer; surface-guided.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

