Diversifying Amino Acids and Peptides via Deaminative Reductive Cross-Couplings Leveraging High-Throughput Experimentation
- PMID: 36853652
- PMCID: PMC10117303
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c11451
Diversifying Amino Acids and Peptides via Deaminative Reductive Cross-Couplings Leveraging High-Throughput Experimentation
Abstract
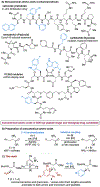
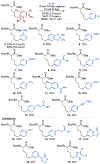
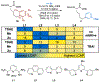
A deaminative reductive coupling of amino acid pyridinium salts with aryl bromides has been developed to enable efficient synthesis of noncanonical amino acids and diversification of peptides. This method transforms natural, commercially available lysine, ornithine, diaminobutanoic acid, and diaminopropanoic acid to aryl alanines and homologated derivatives with varying chain lengths. Attractive features include ability to transverse scales, tolerance of pharma-relevant (hetero)aryls and biorthogonal functional groups, and the applicability beyond monomeric amino acids to short and macrocyclic peptide substrates. The success of this work relied on high-throughput experimentation to identify complementary reaction conditions that proved critical for achieving the coupling of a broad scope of aryl bromides with a range of amino acid and peptide substrates including macrocyclic peptides.
Figures


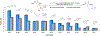

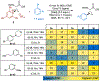


References
-
- Henninot A; Collins JC; Nuss JM, The Current State of Peptide Drug Discovery: Back to the Future? J. Med. Chem 2018, 61 (4), 1382–1414. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00318; - DOI - PubMed
- Raines RT; Wennemers H, Peptides on the Rise. Acc. Chem. Res 2017, 50 (10), 2419–2419. 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00471; - DOI - PubMed
- Sawyer TK, CHAPTER 1 Renaissance in Peptide Drug Discovery: The Third Wave. In Peptide-based Drug Discovery: Challenges and New Therapeutics, The Royal Society of Chemistry: 2017; pp 1–34. 10.1039/9781788011532-00001; - DOI
- Muttenthaler M; King GF; Adams DJ; Alewood PF, Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2021, 20 (4), 309–325. 10.1038/s41573-020-00135-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yanagisawa T; Ishii R; Fukunaga R; Kobayashi T; Sakamoto K; Yokoyama S, Multistep Engineering of Pyrrolysyl-tRNA Synthetase to Genetically Encode Nɛ-(o-Azidobenzyloxycarbonyl) lysine for Site-Specific Protein Modification. Chem. Biol 2008, 15 (11), 1187–1197. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.10.004; - DOI - PubMed
- Young TS; Schultz PG, Beyond the canonical 20 amino acids: expanding the genetic lexicon. J. Biol. Chem 2010, 285 (15), 11039–44. 10.1074/jbc.R109.091306; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Mukai T; Kobayashi T; Hino N; Yanagisawa T; Sakamoto K; Yokoyama S, Adding l-lysine derivatives to the genetic code of mammalian cells with engineered pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2008, 371 (4), 818–822. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.164; - DOI - PubMed
- Nguyen DP; Lusic H; Neumann H; Kapadnis PB; Deiters A; Chin JW, Genetic Encoding and Labeling of Aliphatic Azides and Alkynes in Recombinant Proteins via a Pyrrolysyl-tRNA Synthetase/tRNACUA Pair and Click Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131 (25), 8720–8721. 10.1021/ja900553w; - DOI - PubMed
- Liu CC; Schultz PG, Adding new chemistries to the genetic code. Ann. Rev. Biochem 2010, 79, 413–44. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.052308.105824. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alleyne C; Amin RP; Bhatt B; Bianchi E; Blain JC; Boyer N; Branca D; Embrey MW; Ha SN; Jette K; Johns DG; Kerekes AD; Koeplinger KA; LaPlaca D; Li N; Murphy B; Orth P; Ricardo A; Salowe S; Seyb K; Shahripour A; Stringer JR; Sun Y; Tracy R; Wu C; Xiong Y; Youm H; Zokian HJ; Tucker TJ, Series of Novel and Highly Potent Cyclic Peptide PCSK9 Inhibitors Derived from an mRNA Display Screen and Optimized via Structure-Based Design. J. Med. Chem 2020, 63 (22), 13796–13824. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01084. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li JC; Liu T; Wang Y; Mehta AP; Schultz PG, Enhancing Protein Stability with Genetically Encoded Noncanonical Amino Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140 (47), 15997–16000. 10.1021/jacs.8b07157; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Lang K; Chin JW, Cellular incorporation of unnatural amino acids and bioorthogonal labeling of proteins. Chem. Rev 2014, 114 (9), 4764–806. 10.1021/cr400355w. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

