Generation of gene-of-interest knockouts in murine organoids using CRISPR-Cas9
- PMID: 36853714
- PMCID: PMC9918790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102076
Generation of gene-of-interest knockouts in murine organoids using CRISPR-Cas9
Abstract
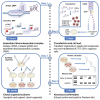
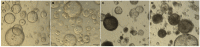
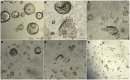
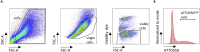
Gene-of-interest knockout organoids present a powerful and versatile research tool to study a gene's effects on many biological and pathological processes. Here, we present a straightforward and broadly applicable protocol to generate gene knockouts in mouse organoids using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. We describe the processes of transient transfecting organoids with pre-assembled CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes, organoid cell sorting, and establishing clonal organoid culture pairs. We then detail how to confirm the knockout via Western blot analysis.
Keywords: CRISPR; Cancer; Organoids.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Eissmann M.F., Dijkstra C., Jarnicki A., Phesse T., Brunnberg J., Poh A.R., Etemadi N., Tsantikos E., Thiem S., Huntington N.D., et al. IL-33-mediated mast cell activation promotes gastric cancer through macrophage mobilization. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:2735. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10676-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artegiani B., Hendriks D., Beumer J., Kok R., Zheng X., Joore I., Chuva de Sousa Lopes S., van Zon J., Tans S., Clevers H. Fast and efficient generation of knock-in human organoids using homology-independent CRISPR-Cas9 precision genome editing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020;22:321–331. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0472-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Artegiani B., van Voorthuijsen L., Lindeboom R.G.H., Seinstra D., Heo I., Tapia P., López-Iglesias C., Postrach D., Dayton T., Oka R., et al. Probing the tumor suppressor function of BAP1 in CRISPR-engineered human liver organoids. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24:927–943.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.04.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drost J., van Boxtel R., Blokzijl F., Mizutani T., Sasaki N., Sasselli V., de Ligt J., Behjati S., Grolleman J.E., van Wezel T., et al. Use of CRISPR-modified human stem cell organoids to study the origin of mutational signatures in cancer. Science. 2017;358:234–238. doi: 10.1126/science.aao3130. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

