In Silico Evaluation of the Thr58-Associated Conserved Water with KRAS Switch-II Pocket Binders
- PMID: 36854010
- PMCID: PMC10015465
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01479
In Silico Evaluation of the Thr58-Associated Conserved Water with KRAS Switch-II Pocket Binders
Abstract
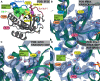
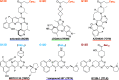
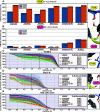
The KRAS switch-II pocket (SII-P) has proven to be one of the most successful tools for targeting KRAS with small molecules to date. This has been demonstrated with several KRAS(G12C)-targeting covalent inhibitors, already resulting in two FDA-approved drugs. Several earlier-stage compounds have also been reported to engage KRAS SII-P with other position 12 mutants, including G12D, G12S, and G12R. A highly conserved water molecule exists in the KRAS SII-P, linking Thr58 of switch-II and Gly10 of β1 sheet. This conserved water is also present in the cocrystal structures of most of the disclosed small-molecule inhibitors but is only displaced by a handful of SII-P binders. Here, we evaluated the conserved water molecule energetics by the WaterMap for the SII-P binders with publicly disclosed structures and studied the water behavior in the presence of selected inhibitors by microsecond timescale molecular dynamics (MD) simulations using two water models (total simulation time of 120 μs). Our data revealed the high-energy nature of this hydration site when coexisting with an SII-P binder and that there is a preference for a single isolated hydration site in this location within the most advanced compounds. Furthermore, water displacement was only achieved with a few disclosed compounds and was suboptimal, as for instance a cyanomethyl group as a water displacer appears to introduce repulsion with the native conformation of Thr58. These results suggested that this conserved water should be considered more central when designing new inhibitors, especially in the design of noncovalent inhibitors targeting the SII-P.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
KRAS is vulnerable to reversible switch-II pocket engagement in cells.Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Jun;18(6):596-604. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-00985-w. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Nat Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35314814 Free PMC article.
-
Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulation to Gain Insight Into the Binding of MRTX1133 and Trametinib With KRASG12D Mutant Protein for Drug Repurposing.J Mol Recognit. 2024 Nov;37(6):e3103. doi: 10.1002/jmr.3103. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Mol Recognit. 2024. PMID: 39318275
-
Modeling receptor flexibility in the structure-based design of KRASG12C inhibitors.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2022 Aug;36(8):591-604. doi: 10.1007/s10822-022-00467-0. Epub 2022 Aug 5. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2022. PMID: 35930206 Free PMC article.
-
Small-Molecule Inhibitors Directly Targeting KRAS as Anticancer Therapeutics.J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 10;63(23):14404-14424. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01312. Epub 2020 Nov 23. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33225706 Review.
-
Targeting KRAS in non-small-cell lung cancer: recent progress and new approaches.Ann Oncol. 2021 Sep;32(9):1101-1110. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Ann Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34089836 Review.
Cited by
-
Binding modes of the KRAS(G12C) inhibitors GDC-6036 and LY3537982 revealed by all atom molecular dynamics simulations.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 10;15(1):24843. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07532-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40640254 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent-Allosteric Inhibitors: Do We Get the Best of Both Worlds?J Med Chem. 2025 Feb 27;68(4):4040-4052. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02760. Epub 2025 Feb 12. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39937154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Receptor Desolvation Scoring and Covalent Sampling in DOCK 6: Methods Evaluated on a RAS Test Set.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jan 27;65(2):722-748. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01623. Epub 2025 Jan 6. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 39757424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ostrem J. M. L.; Shokat K. M. Targeting KRAS G12C with Covalent Inhibitors. Ann. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2022, 6, 49–64. 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-041621-012549. - DOI
-
- Nakajima E. C.; Drezner N.; Li X.; Mishra-Kalyani P. S.; Liu Y.; Zhao H.; Bi Y.; Liu J.; Rahman A.; Wearne E.; Ojofeitimi I.; Hotaki L. T.; Spillman D.; Pazdur R.; Beaver J. A.; Singh H. FDA Approval Summary: Sotorasib for KRAS G12C-Mutated Metastatic NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1482–1486. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Adagrasib for KRAS G12C-Mutated NSCLC. FDA; 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/216340Orig...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

