Prevalence and risk factors of hypothyroidism after universal salt iodisation: a large cross-sectional study from 31 provinces of China
- PMID: 36854590
- PMCID: PMC9980360
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064613
Prevalence and risk factors of hypothyroidism after universal salt iodisation: a large cross-sectional study from 31 provinces of China
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the prevalence and risk factors of hypothyroidism after universal salt iodisation for 20 years in mainland China.
Design: Nationwide, cross-sectional survey.
Setting and participants: The Thyroid Disorders, Iodine Status and Diabetes epidemiological study included adults from 31 provinces of China. Data included demographic, physical characteristics, urine, serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroid-peroxidase antibody (TPOAb), thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb) and thyroid ultrasonography. Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) was classified into severe SCH (TSH >10 mU/L) and mild SCH (TSH 4.2-9.9 mU/L). A total of 78 470 (38 182 men and 40 288 women) participants were included in the final analysis.
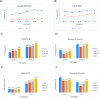
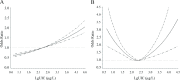
Results: The prevalence of hypothyroidism was 13.95%. The prevalence rates of overt hypothyroidism (OH) and SCH were 1.02% and 13.93%, which mild SCH was significantly higher than severe SCH (12.18% vs 0.75%). Prevalence was higher in women than in men, and this gender difference was noted among all age groups. The prevalence of mild SCH, severe SCH and OH increases by 1.16%, 1.40% and 1.29% for every 10 years older. TPOAb or/and TgAb positive were significantly associated with OH and severe SCH (OR 15.9, p<0.001). However, SCH was positively correlated with increased urine iodine concentration, but this correlation was only in antibody-negative female patients. In non-autoimmune and male populations, there was a U-shaped relationship between severe SCH and OH and urine iodine concentration.
Conclusions: Mild SCH is the most common form of hypothyroidism, which is related to iodine intake. Severe SCH is more similar to OH which autoimmune is the main cause. The various effects of iodine on hypothyroidism depend on thyroid autoimmune and gender.
Keywords: Diabetes & endocrinology; EPIDEMIOLOGY; Thyroid disease.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
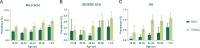

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
