Comparison of modified anterior and traditional posterior accesses for ultrasound-guided superior laryngeal nerve block in awake endotracheal intubation: study protocol for a randomised non-inferiority clinical trial
- PMID: 36854598
- PMCID: PMC9980353
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068779
Comparison of modified anterior and traditional posterior accesses for ultrasound-guided superior laryngeal nerve block in awake endotracheal intubation: study protocol for a randomised non-inferiority clinical trial
Abstract
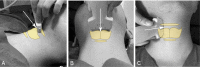
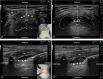
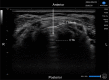
Introduction: Awake tracheal intubation (ATI) involves placing a tracheal tube in an awake, spontaneously breathing patient. Superior laryngeal nerve block (SLNB) can effectively abolish the glottic closure reflex, and blunt the sensation of the structures above the cords. A method that consists of SLNB along with translaryngeal injection (TLI) can provide satisfactory anaesthesia and intubating conditions. We present a novel modified access of SLNB, ultrasound (US)-guided anterior SLNB, to aid awake videolaryngoscopes-assisted endotracheal intubation in adult elective surgery patients, and we compare the effectiveness and safety to traditional US-guided posterior SLNB.
Methods and analysis: A total of 100 adult elective surgery patients requiring general endotracheal anaesthesia will be randomly assigned to the modified group (modified US-guided anterior SLNB) or the traditional group (traditional US-guided posterior SLNB). After SLNB, all participants will be performed with TLI. The primary outcome is the proportion of acceptable intubation conditions based on intubation scores. Secondary outcomes include: (a) the first-attempt intubation success rate, (b) haemodynamic changes during ATI, (c) time taken for airway anaesthesia and intubation, (d) recall of intubation, (e) participant perception of comfort during intubation, (f) perioperative complication rate. This report describes the study design of this randomised controlled trial.
Ethics and dissemination: The study protocol has been approved by an ethical committee of the West China Hospital (Sichuan University), and registered at the Chinese Clinical Trials Register (www.chictr.org.cn). Results will be published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2200058086.
Keywords: adult anaesthesia; adult intensive & critical care; pain management; ultrasonography.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modified anterior approach versus traditional posterior approach for ultrasound-guided superior laryngeal nerve block in awake endotracheal intubation: a randomized non-inferiority clinical trial.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2264856. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2264856. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37813093 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Application of Ultrasound-Guided Internal Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block in Patients with Severe COPD Undergoing Awake Fibreoptic Nasotracheal Intubation: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Apr 6;18:521-532. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S399513. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37056682 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of ultrasound-guided internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve block on postoperative sore throat induced by a NIM-EMG-ETT: study protocol for a double-blinded randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Nov 8;25(1):746. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08591-y. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39516826 Free PMC article.
-
Airway nerve blocks for awake tracheal intubation: A meta-analysis of randomized control trials and trial sequential analysis.J Clin Anesth. 2023 Sep;88:111122. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2023.111122. Epub 2023 Apr 11. J Clin Anesth. 2023. PMID: 37054484
-
The efficacy of ultrasound-guided superior laryngeal nerve block on postoperative sore throat after endotracheal intubation under general anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian J Surg. 2023 Nov;46(11):4778-4779. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2023.05.008. Epub 2023 May 19. Asian J Surg. 2023. PMID: 37211437 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Modified anterior approach versus traditional posterior approach for ultrasound-guided superior laryngeal nerve block in awake endotracheal intubation: a randomized non-inferiority clinical trial.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2264856. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2264856. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37813093 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Success rates of endotracheal intubation using the standard method versus the modified-ramped position.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Sep 27;85(11):5491-5496. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001331. eCollection 2023 Nov. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37915676 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
