Fine mapping spatiotemporal mechanisms of genetic variants underlying cardiac traits and disease
- PMID: 36854752
- PMCID: PMC9975214
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36638-2
Fine mapping spatiotemporal mechanisms of genetic variants underlying cardiac traits and disease
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Fine mapping spatiotemporal mechanisms of genetic variants underlying cardiac traits and disease.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 20;14(1):4370. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40048-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37474502 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
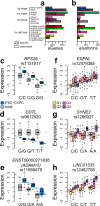
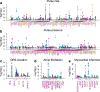
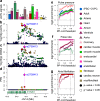
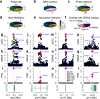
The causal variants and genes underlying thousands of cardiac GWAS signals have yet to be identified. Here, we leverage spatiotemporal information on 966 RNA-seq cardiac samples and perform an expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) analysis detecting eQTLs considering both eGenes and eIsoforms. We identify 2,578 eQTLs associated with a specific developmental stage-, tissue- and/or cell type. Colocalization between eQTL and GWAS signals of five cardiac traits identified variants with high posterior probabilities for being causal in 210 GWAS loci. Pulse pressure GWAS loci are enriched for colocalization with fetal- and smooth muscle- eQTLs; pulse rate with adult- and cardiac muscle- eQTLs; and atrial fibrillation with cardiac muscle- eQTLs. Fine mapping identifies 79 credible sets with five or fewer SNPs, of which 15 were associated with spatiotemporal eQTLs. Our study shows that many cardiac GWAS variants impact traits and disease in a developmental stage-, tissue- and/or cell type-specific fashion.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Loots GG, et al. Identification of a coordinate regulator of interleukins 4, 13, and 5 by cross-species sequence comparisons. Science. 2000;288:136–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

