Prospective cohort study on mesh shrinkage measured with MRI after robot-assisted minimal invasive retrorectus ventral hernia repair using an iron-oxide-loaded polyvinylidene fluoride mesh
- PMID: 36854798
- PMCID: PMC10234924
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-023-09938-3
Prospective cohort study on mesh shrinkage measured with MRI after robot-assisted minimal invasive retrorectus ventral hernia repair using an iron-oxide-loaded polyvinylidene fluoride mesh
Abstract
Background: Mesh-reinforced ventral hernia repair is considered the gold standard treatment for all but the smallest of hernias. Human data on mesh shrinkage in the retrorectus mesh position is lacking. A prospective observational cohort study was performed to measure mesh shrinkage in robot-assisted minimal invasive retrorectus repair of ventral hernias.
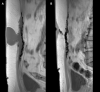
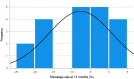
Methods: A cohort of 20 patients underwent a robot-assisted minimal invasive retrorectus repair of their ventral hernia. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) imaging was performed one month and thirteen months after implantation of an iron-oxide-impregnated polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) mesh to assess the decrease in mesh surface area. Inter-rater reliability among three radiologists regarding measurement of the mesh dimensions was analyzed. Quality of Life scoring was evaluated.
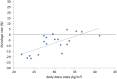
Results: The inter-rater reliability between the radiologists reported as the intra-class correlations proved to be excellent for mesh width (ICC 0.95), length (ICC 0.98) and surface area (ICC 0.99). Between MRI measurements at one month and thirteen months postoperatively, there was a significant increase in mesh surface area (+ 12.0 cm2, p = 0.0013) and mesh width (+ 0.8 cm, p < 0.001), while the length of the mesh remained unchanged (-0.1 cm, p = 0.754). Quality of Life Scoring showed a significant improvement in Quality of Life after one month and a further improvement at thirteen months (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: There was an excellent inter-rater reliability between three radiologists when measuring width, length, and surface area of an iron-oxide-impregnated PVDF mesh using MRI visualization. Mesh shrinkage was not observed, instead the effective mesh surface area and width of the mesh increased.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03380312.
Keywords: Mesh shrinkage; Polyvinylidene fluoride; Retromuscular; Retrorectus; Ventral hernia; Visible mesh.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors received a research grant from FEG textiltechnik the company producing the Dynamesh visible that was used in the study. This was mainly used for financing the MRI studies and the statistical analysis performed. The company had no influence on the initiation, the conduct and the manuscript preparation of the results. Outside of the study Maaike Vierstraete, Roel Beckers, Lorenz Vangeel, Brend Foriers and Pieter Pletinckx report no conflict of interest. Filip Muysoms reports having received research grants from Medtronic, Intuitive Surgical and FEG Textiltechnik, speakers’ honoraria from Medtronic, Bard Davol, Intuitive Surgical, FEG Textiltechnik and WL GORE & ass, consultancy honoraria from Sofradim, CMR surgical.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

