RNA-seq reveals novel mechanistic targets of Livin in bladder cancer
- PMID: 36855119
- PMCID: PMC9976429
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-023-01194-w
RNA-seq reveals novel mechanistic targets of Livin in bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer is a very common malignancy with a high recurrence rate. The survival of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer is poor, and new therapies are needed. Livin has been reported to be upregulated in bladder cancer and influence the proliferation of cancer cells.
Materials and methods: The Livin gene in human bladder cancer cell line T24 was knocked out, and the differentially expressed genes were identified by RNA-seq and qPCR.
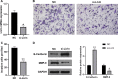
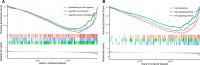
Results: Livin knockdown affects gene expression and has strong negative effects on some cancer-promoting pathways. Furthermore, combined with bladder cancer clinical sample data downloaded from TCGA and GEO, 2 co-up-regulated genes and 58 co-down-regulated genes were identified and validated, which were associated with cancer proliferation and invasion.
Conclusion: All these results suggest that Livin plays an important role in bladder cancer and could be a potential anticancer target in clinical therapy.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Livin; RNA-seq; T24 cell.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Suppression of livin gene expression by siRNA leads to growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in human bladder cancer T24 cells.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(5):1039-44. doi: 10.1271/bbb.90934. Epub 2010 May 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20460713
-
Livin may serve as a marker for prognosis of bladder cancer relapse and a target of bladder cancer treatment.Urol Oncol. 2009 May-Jun;27(3):277-83. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.03.015. Epub 2008 Jun 16. Urol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 18555709
-
[Effects of gene Livin transfection affect on the apoptosis in bladder carcinoma cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Mar 25;88(12):853-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18756993 Chinese.
-
Complexity, retinoid-responsive gene networks, and bladder carcinogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;462:449-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4737-2_35. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10599447 Review.
-
Targeted therapies in bladder cancer: an overview of in vivo research.Nat Rev Urol. 2015 Dec;12(12):681-94. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2015.231. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Nat Rev Urol. 2015. PMID: 26390971 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

