Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Hydantoins
- PMID: 36855589
- PMCID: PMC9954259
- DOI: 10.1021/acsorginorgau.1c00058
Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Hydantoins
Abstract
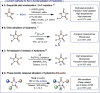
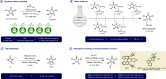
A highly efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly protocol is reported for the C5-selective alkylation of hydantoins under phase-transfer catalysis. The reactions are scalable and only require a catalytic amount of tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBAB) to achieve high yields under mild reaction conditions. Moreover, the method is applicable to a wide range of electrophiles, including alkyl-, allyl-, propargyl-, and benzyl halides, as well as acrylates and dibromoalkanes, but also to virtually any hydantoin precursor. We also highlight the potential for an enantioselective adaptation using a chiral phase-transfer catalyst.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
