B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune diseases: Monoclonal antibodies or chimeric antigen receptor-based therapy?
- PMID: 36855629
- PMCID: PMC9968396
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1126421
B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune diseases: Monoclonal antibodies or chimeric antigen receptor-based therapy?
Abstract
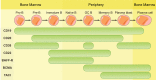
Immune system detects foreign pathogens, distinguishes them from self-antigens and responds to defend human body. When this self-tolerance is disrupted, the overactive immune system attacks healthy tissues or organs and the autoimmune diseases develop. B cells and plasma cells contribute a lot to pathogenesis and persistence of autoimmune diseases in both autoantibody-dependent and autoantibody-independent ways. Accumulating data indicates that treatments aiming to eliminate antibody-secreting cells (B cells or plasma cells) are effective in a wide spectrum of autoimmune diseases. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) deplete B cell lineage or plasma cells by signaling disruption, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Engineered-T cells armed with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) have been adopted from field of hematological malignancies as a method to eliminate B cells or plasma cells. In this review, we update our understanding of B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune diseases, review the mechanism, efficacy, safety and application of monoclonal antibodies and CAR-based immunotherapies, and discuss the strengths and weaknesses of these treatment options for patients.
Keywords: B cell depletion; autoimmune disease; chimeric antigen receptor; immunotherapy; monoclonal antibody.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Xu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical