Application of microfluidic technologies on COVID-19 diagnosis and drug discovery
- PMID: 36855672
- PMCID: PMC9951611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.014
Application of microfluidic technologies on COVID-19 diagnosis and drug discovery
Abstract
The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has boosted the development of antiviral research. Microfluidic technologies offer powerful platforms for diagnosis and drug discovery for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) diagnosis and drug discovery. In this review, we introduce the structure of SARS-CoV-2 and the basic knowledge of microfluidic design. We discuss the application of microfluidic devices in SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis based on detecting viral nucleic acid, antibodies, and antigens. We highlight the contribution of lab-on-a-chip to manufacturing point-of-care equipment of accurate, sensitive, low-cost, and user-friendly virus-detection devices. We then investigate the efforts in organ-on-a-chip and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) synthesizing chips in antiviral drug screening and mRNA vaccine preparation. Microfluidic technologies contribute to the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 research efforts and provide tools for future viral outbreaks.
Keywords: COVID-19; Detection; Drug screen; Lab-on-a-chip; Microfluidic; Organ-on-a-chip; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
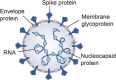




Similar articles
-
A materials-science perspective on tackling COVID-19.Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5(11):847-860. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-00247-y. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Nat Rev Mater. 2020. PMID: 33078077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Organs-on-a-Chip for Modeling Human Infectious Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Sep 21;54(18):3550-3562. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00411. Epub 2021 Aug 29. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34459199
-
[Applications of separation technology in novel coronavirus research, epidemic prevention and detection].Se Pu. 2021 Jul 8;39(7):679-685. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.03022. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227364 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) and Its Integration into Nanomedicine and Microfluidic Devices as Point-of-Care Testing (POCT).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 16;24(12):10233. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210233. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulling-Force Spinning Top for Serum Separation Combined with Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices in COVID-19 ELISA Diagnosis.ACS Sens. 2021 Jul 23;6(7):2709-2719. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c00773. Epub 2021 Jul 15. ACS Sens. 2021. PMID: 34263598
Cited by
-
Lymph Node-on-Chip Technology: Cutting-Edge Advances in Immune Microenvironment Simulation.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 16;16(5):666. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050666. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic biosensors for biomarker detection in body fluids: a key approach for early cancer diagnosis.Biomark Res. 2024 Dec 5;12(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00697-4. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39639411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis of bovine rotavirus: an overview of currently available methods.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1550601. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1550601. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40092041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for Improved pDNA Loading and Protection Using Cationic and Neutral LNPs with Industrial Scalability Potential Using Microfluidic Technology.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 14;19:4235-4251. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S457302. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38766661 Free PMC article.
-
The Development of Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticle Lateral Flow Test Strips for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S Proteins on the Surface of Cold-Chain Food Packaging.Molecules. 2024 Apr 13;29(8):1776. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081776. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gates B. Responding to Covid-19 – a once-in-a-century pandemic? N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1677–1679. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

