Randomized controlled trial of nalfurafine for refractory pruritus in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 36856148
- PMCID: PMC9980412
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2175590
Randomized controlled trial of nalfurafine for refractory pruritus in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
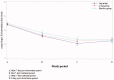
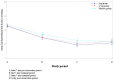
Background: Chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus (CKD-aP) is very common and sometimes refractory to treatment in hemodialysis patients. In a trial conducted in Japan, nalfurafine, effectively reduced itching of treatment-resistant CKD-aP. Our present bridging study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nalfurafine in Chinese cohort with refractory CKD-aP.Methods: In this phase III, multicenter bridging study conducted at 22 sites in China, 141 Chinese cases with refractory CKD-aP were randomly (2:2:1) assigned to receive 5 μg, 2.5 μg of nalfurafine or a placebo orally for 14 days in a double-blind manner. The primary end point was the mean decrease in the mean visual analogue scale (VAS) from baseline.Results: A total of 141 patients were included. The primary endpoint analysis based on full analysis set (FAS), the difference of mean VAS decrease between 5 μg nalfurafine and placebo group was 11.37 mm (p = .041); the difference of mean VAS decrease between 2.5 μg and placebo group was 8.81 mm, but not statistically significantly different. Both differences were greater than 4.13 mm, which met its predefined success criterion of at least 50% efficacy of the key Japanese clinical trial. The per protocol set (PPS) analysis got similar results. The incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) was 49.1% in 5μg, 38.6% in 2.5 μg and 33.3% in placebo group. The most common ADR was insomnia, seen in 21 of the 114 nalfurafine patients.Conclusions: Oral nalfurafine effectively reduced itching with few significant ADRs in Chinese hemodialysis patients with refractory pruritus.
Keywords: Nalfurafine; chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus; clinical trial; hemodialysis; kappa opioid receptor agonist; refractory.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of a novel kappa-receptor agonist, nalfurafine hydrochloride, on severe itch in 337 haemodialysis patients: a Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010 Apr;25(4):1251-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp588. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010. PMID: 19926718 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of nalfurafine hydrochloride in patients with chronic liver disease with refractory pruritus: A randomized, double-blind trial.Hepatol Res. 2017 Sep;47(10):972-982. doi: 10.1111/hepr.12830. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Hepatol Res. 2017. PMID: 27753159
-
Clinical Profiles of Nalfurafine Hydrochloride for the Treatment of Pruritus Patients.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;271:455-472. doi: 10.1007/164_2020_400. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33201326
-
Nalfurafine hydrochloride to treat pruritus: a review.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015 May 11;8:249-55. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S55942. eCollection 2015. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26005355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nalfurafine hydrochloride: a new drug for the treatment of uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients.Drugs Today (Barc). 2009 May;45(5):323-9. doi: 10.1358/dot.2009.45.5.1362067. Drugs Today (Barc). 2009. PMID: 19584962 Review.
Cited by
-
[Clinical Research Progress on Using κ-Opioid Receptor Agonists to Treat Uremic Pruritus].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jul 20;55(4):1044-1048. doi: 10.12182/20240760506. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39170011 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Anxiety and depression in geriatric hemodialysis patients: factors that influence the border of diseases.Front Psychol. 2023 Nov 24;14:1281878. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1281878. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38078242 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Outcomes of Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus: International Results from Peritoneal Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Dec 1;19(12):1622-1634. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000537. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39652652
-
Discovery of Potent Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonists Derived from Akuammicine.J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 12;67(23):20842-20857. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00736. Epub 2024 Nov 20. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39565354
-
Efficacy and safety of different systemic drugs in the treatment of uremic pruritus among hemodialysis patients: a network meta-analysis based on randomized clinical trials.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 5;11:1334944. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1334944. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38646551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mettang T, Kremer AE.. Uremic pruritus. Kidney Int. 2015;87(4):685–691. - PubMed
-
- Solak Y, Biyik Z, Atalay H, et al. . Pregabalin versus gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pruritus in maintenance haemodialysis patients: a prospective, crossover study. Nephrology. 2012;17(8):710–717. - PubMed
-
- Pisoni RL, Wikstrom B, Elder SJ, et al. . Pruritus in haemodialysis patients: international results from the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study (DOPPS). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21(12):3495–3505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous