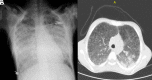
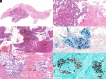
Fatal Invasive Aspergillosis in a Child with Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis
- PMID: 36856362
- PMCID: PMC10081066
- DOI: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2023.22178
Fatal Invasive Aspergillosis in a Child with Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
