Immunocompromised Host Pneumonia: Definitions and Diagnostic Criteria: An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report
- PMID: 36856712
- PMCID: PMC9993146
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202212-1019ST
Immunocompromised Host Pneumonia: Definitions and Diagnostic Criteria: An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report
Abstract
Pneumonia imposes a significant clinical burden on people with immunocompromising conditions. Millions of individuals live with compromised immunity because of cytotoxic cancer treatments, biological therapies, organ transplants, inherited and acquired immunodeficiencies, and other immune disorders. Despite broad awareness among clinicians that these patients are at increased risk for developing infectious pneumonia, immunocompromised people are often excluded from pneumonia clinical guidelines and treatment trials. The absence of a widely accepted definition for immunocompromised host pneumonia is a significant knowledge gap that hampers consistent clinical care and research for infectious pneumonia in these vulnerable populations. To address this gap, the American Thoracic Society convened a workshop whose participants had expertise in pulmonary disease, infectious diseases, immunology, genetics, and laboratory medicine, with the goal of defining the entity of immunocompromised host pneumonia and its diagnostic criteria.
Keywords: diagnosis; immunocompromised host; immunosuppression; pneumonia.
Figures
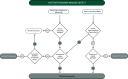
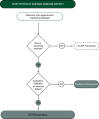
References
-
- Harpaz R, Dahl RM, Dooling KL. Prevalence of immunosuppression among US adults, 2013. JAMA . 2016;316:2547–2548. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS. 2022. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

