Bias in Gene-by-Environment Interaction Effects with Sum Scores; An Application to Well-being Phenotypes
- PMID: 36856918
- PMCID: PMC10275801
- DOI: 10.1007/s10519-023-10137-y
Bias in Gene-by-Environment Interaction Effects with Sum Scores; An Application to Well-being Phenotypes
Abstract
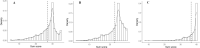
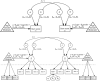
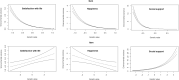
In the current study, we investigated the influence of using skewed sum scores on estimated gene-by-environment interaction effects (GxE) for life satisfaction and happiness with perceived social support. To this end, we analyzed item-level data from a large adult twin sample (Ns between 3610 and 11,305) of the Netherlands Twin Register. Item response theory (IRT) models were incorporated in unmeasured (univariate) GxE models, and measured GxE models (with social support as moderator). We found that skewness introduced spurious GxE effects, with the largest effect for the most skewed variable (social support). Finally, in the IRT model for life satisfaction, but not for happiness, heritability estimates decreased with higher social support, while this was not observed when analyzing sum scores. Together, our results indicate that IRT can be used to address psychometric issues related to the use of sum scores, especially in the context of GxE, for complex traits like well-being.
Keywords: Genotype by environment interaction; Item Response Theory; Measurement error; Sum scores; Twin studies; Well-being.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dependence of Gene-by-Environment Interactions (GxE) on Scaling: Comparing the Use of Sum Scores, Transformed Sum Scores and IRT Scores for the Phenotype in Tests of GxE.Behav Genet. 2016 Jul;46(4):552-72. doi: 10.1007/s10519-016-9783-5. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Behav Genet. 2016. PMID: 26833465
-
Psychometric Modelling of Longitudinal Genetically Informative Twin Data.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 16;10:837. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00837. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31681400 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical Ability and Socio-Economic Background: IRT Modeling to Estimate Genotype by Environment Interaction.Twin Res Hum Genet. 2017 Dec;20(6):511-520. doi: 10.1017/thg.2017.59. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 29103406 Free PMC article.
-
GxE effects of FKBP5 and traumatic life events on PTSD: A meta-analysis.J Affect Disord. 2019 Jan 15;243:455-462. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.09.058. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30273884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Narrative review of genes, environment, and cigarettes.Ann Med. 2016 Aug;48(5):337-51. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2016.1177196. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Ann Med. 2016. PMID: 27124093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using genomic structural equation modeling to examine the genetic architecture of PTSD and life satisfaction phenotypes.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2025 Dec;16(1):2463187. doi: 10.1080/20008066.2025.2463187. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2025. PMID: 39937039 Free PMC article.
-
Practical Implications of Sum Scores Being Psychometrics' Greatest Accomplishment.Psychometrika. 2024 Dec;89(4):1148-1169. doi: 10.1007/s11336-024-09988-z. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Psychometrika. 2024. PMID: 39031300
-
Gene-environment interaction in ADHD traits: the role of school environment, personality, callousness-unemotional traits and satisfaction with life.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2025 Jul;34(7):2205-2214. doi: 10.1007/s00787-024-02628-y. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39760858 Free PMC article.
-
The Heritability of Psychopathology Symptoms in Early Adolescence: Moderation by Family Cultural Values in the ABCD Study.Behav Genet. 2024 Jan;54(1):119-136. doi: 10.1007/s10519-023-10154-x. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Behav Genet. 2024. PMID: 37702839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Box GEP, Tiao GC (2011) Bayesian inference in statistical analysis. Wiley
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

