Performance of the European Society of Cardiology 0/1-Hour Algorithm With High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Among Patients With Known Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 36857071
- PMCID: PMC9979014
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.0031
Performance of the European Society of Cardiology 0/1-Hour Algorithm With High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Among Patients With Known Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
Importance: The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 0/1-hour algorithm is a validated high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) protocol for emergency department patients with possible acute coronary syndrome. However, limited data exist regarding its performance in patients with known coronary artery disease (CAD; prior myocardial infarction [MI], coronary revascularization, or ≥70% coronary stenosis).
Objective: To evaluate and compare the diagnostic performance of the ESC 0/1-hour algorithm for 30-day cardiac death or MI among patients with and without known CAD and determine if the algorithm could achieve the negative predictive value rule-out threshold of 99% or higher.
Design, setting, and participants: This was a preplanned subgroup analysis of the STOP-CP prospective multisite cohort study, which was conducted from January 25, 2017, through September 6, 2018, at 8 emergency departments in the US. Patients 21 years or older with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome without ST-segment elevation on initial electrocardiogram were included. Analysis took place between February and December 2022.
Interventions/exposures: Participants with 0- and 1-hour high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) measures were stratified into rule-out, observation, and rule-in zones using the ESC 0/1-hour hs-cTnT algorithm.
Main outcomes and measures: Cardiac death or MI at 30 days determined by expert adjudicators.
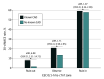
Results: During the study period, 1430 patients were accrued. In the cohort, 775 individuals (54.2%) were male, 826 (57.8%) were White, and the mean (SD) age was 57.6 (12.8) years. At 30 days, cardiac death or MI occurred in 183 participants (12.8%). Known CAD was present in 449 (31.4%). Among patients with known CAD, the ESC 0/1-hour algorithm classified 178 of 449 (39.6%) into the rule-out zone compared with 648 of 981 (66.1%) without CAD (P < .001). Among rule-out zone patients, 30-day cardiac death or MI occurred in 6 of 178 patients (3.4%) with known CAD and 7 of 648 (1.1%) without CAD (P < .001). The negative predictive value for 30-day cardiac death or MI was 96.6% (95% CI, 92.8-98.8) among patients with known CAD and 98.9% (95% CI, 97.8-99.6) in patients without known CAD (P = .04).
Conclusions and relevance: Among patients with known CAD, the ESC 0/1-hour hs-cTnT algorithm was unable to safely exclude 30-day cardiac death or MI. This suggests that clinicians should be cautious if using the algorithm in patients with known CAD. The negative predictive value was significantly higher in patients without a history of CAD but remained less than 99%.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Critical Appraisal of the Negative Predictive Performance of the European Society of Cardiology 0/1-Hour Algorithm for Evaluating Patients With Chest Pain in the US.JAMA Cardiol. 2023 Apr 1;8(4):314-316. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.0043. JAMA Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36857061 No abstract available.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. ; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56-e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. ; Writing Committee Members . 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;78(22):e187-e285. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.07.053 - DOI - PubMed
-
- National hospital ambulatory medical care survey: 2017 emergency department summary tables. National Center for Health Statistics. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhamcs/web_tables/2017_ed_web_tables-508.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

