Using a latent Hawkes process for epidemiological modelling
- PMID: 36857340
- PMCID: PMC9977047
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281370
Using a latent Hawkes process for epidemiological modelling
Abstract
Understanding the spread of COVID-19 has been the subject of numerous studies, highlighting the significance of reliable epidemic models. Here, we introduce a novel epidemic model using a latent Hawkes process with temporal covariates for modelling the infections. Unlike other models, we model the reported cases via a probability distribution driven by the underlying Hawkes process. Modelling the infections via a Hawkes process allows us to estimate by whom an infected individual was infected. We propose a Kernel Density Particle Filter (KDPF) for inference of both latent cases and reproduction number and for predicting the new cases in the near future. The computational effort is proportional to the number of infections making it possible to use particle filter type algorithms, such as the KDPF. We demonstrate the performance of the proposed algorithm on synthetic data sets and COVID-19 reported cases in various local authorities in the UK, and benchmark our model to alternative approaches.
Copyright: © 2023 Lamprinakou et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
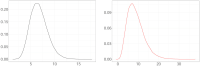
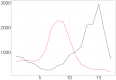
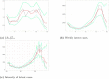
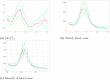


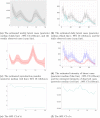
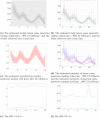
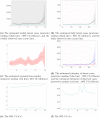
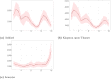
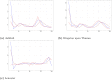
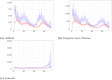
References
-
- Ferguson, N., Laydon, D., Nedjati Gilani, G., Imai, N., Ainslie, K., Baguelin, M., et al. Report 9: Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) to reduce COVID-19 mortality and healthcare demand. (Imperial College in London, 2020). 10.25561/77482 - DOI
-
- Chen, Y., Cheng, J., Jiang, Y. & Liu, K. A time delay dynamic system with external source for the local outbreak of 2019-nCoV. Applicable Analysis. pp. 1-12 (2020)
-
- Zou, D., Wang, L., Xu, P., Chen, J., Zhang, W. & Gu, Q. Epidemic Model Guided Machine Learning for COVID-19 Forecasts in the United States. MedRxiv. (2020), https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/05/25/2020.05.24.20111989
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

